Overview
In this writeup, the goal is to walk through a third approach (in addition to adjusting for covariates and propensity score weighting ) you can take towards tackling the issue of confounding . The following diagram illustrates what we’re hoping to achieve:
We want to estimate the (average) causal effect of Catholic Schooling \(D\) on Post-Grad Earnings \(Y\) .
However, there is an unmeasured covariate , Work Ethic \(X\) (a fork relative to \(D \leftarrow X \rightarrow Y\) ), which is confounding this effect \(D \rightarrow Y\) .
So, as Angrist and Krueger (1991 ) proposed, we can “work around” this confounding (literally, given how the diagram is set up) by using day of birth relative to school cohort as an instrument :
Since this day of birth has no direct causal relationship with work ethic, and
Has no direct causal relationship with Post-Grad Earnings (only an indirect effect on it through Catholic Schooling \(D\) ),
This cohort-relative date of birth can play the same role that a random coin flip plays in the “gold standard” of randomized medical trials!
Under these assumptions (which need to be argued for! And are argued for in Angrist and Krueger (1991 ) ), we can recover the causal effect of \(D\) on \(Y\) via the “classical IV estimator”:
\[
\beta_{\text{IV}}^{D \rightarrow Y} = \frac{\text{Cov}[Z,Y]}{\text{Cov}[D,Y]}
\]
In this writeup, we will generate simulated data on birthdates, school-dropout behavior, and eventual earnings, then use the above IV estimator formula to recover the causal effect of Catholic Schooling on Post-Grad Earnings. We can then verify the accuracy of this estimate, since we generated the data in the first place! The beauty of generative modeling 😉
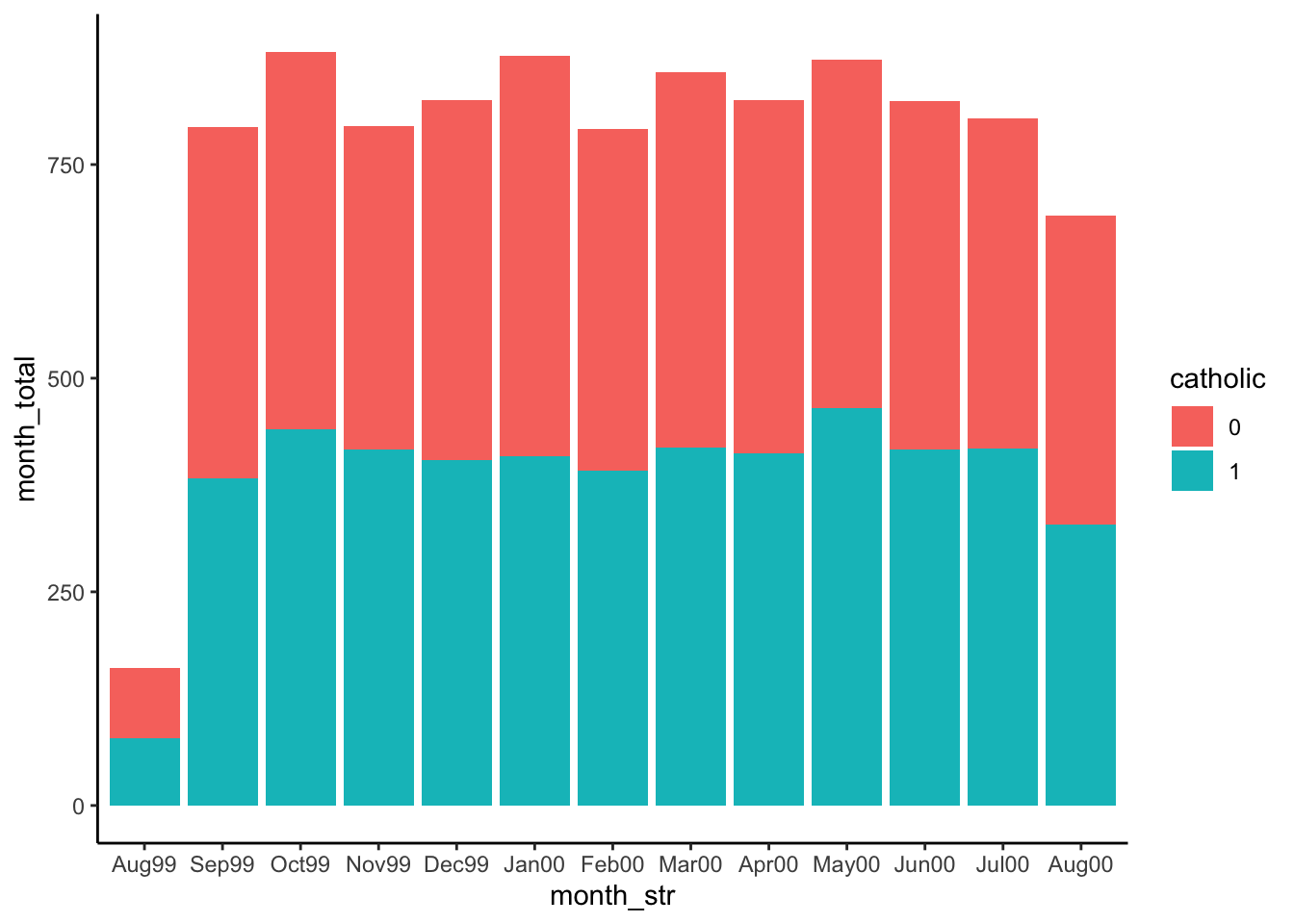
Number of Students Per Month
Code
<- student_df |> group_by (month_str, catholic) |> summarize (month_total= n ())|> ggplot (aes (x= month_str,y= month_total, fill= catholic)) + geom_bar (stat= 'identity' ) + theme_classic ()
Now the Dropping-Out Simulation
First day of school year: Aug 26
Last day of school: Jun 18
\(\implies\) This cohort = all who turn 5 yrs old between Aug 27 2004 and Aug 26 2005\(\implies\) All born between Aug 27 1999 and Aug 26 2000
Code
<- student_df |> mutate (can_drop_out = as.numeric (turns_18 <= lubridate:: make_date (2018 , 6 , 18 ))|> group_by (dob) |> summarize (sum (can_drop_out)) |> head ()
1999-08-26
25
1999-08-27
30
1999-08-28
30
1999-08-29
29
1999-08-30
23
1999-08-31
24
What percentage of students will actually have a chance to drop out? i.e., What proportion of students are born so that they turn 18 before the last day of school?
Code
<- student_df |> summarize (elig_prop= mean (can_drop_out)) |> pull ())
Code
# National mean 8.6% <- 0.086 <- (1 / elig_prop) * raw_dropout_rate)
Code
# Simulate desire to drop out set.seed (5651 )<- rbern (nrow (student_df), prob= dropout_rate)$ wants_to_drop <- wtd_vals<- student_df |> mutate (dropout = as.numeric (wants_to_drop== 1 & can_drop_out== 1 )mean (student_df$ dropout)
Code
|> group_by (turns_18) |> summarize (dob_dropouts= sum (dropout),wants_dropout= sum (wants_to_drop),total= n (), |> head ()
2017-08-25
1
1
25
2017-08-26
5
5
30
2017-08-27
7
7
30
2017-08-28
3
3
29
2017-08-29
1
1
23
2017-08-30
3
3
24
Compute Cumulative Number of Dropouts Over Time
Code
<- student_df |> group_by (dob, catholic) |> summarize (dob_dropout= sum (dropout)
`summarise()` has grouped output by 'dob'. You can override using the `.groups`
argument.
Code
#dob_df$drop_todate <- cumsum(dob_df$dob_dropout) #dob_df |> group_by(catholic) |> summarize(drop_todate=cumsum(dob_dropout)) |> ungroup() <- dob_df |> group_by (catholic) |> arrange (dob) |> mutate (drop_todate= cumsum (dob_dropout)) |> ungroup ()
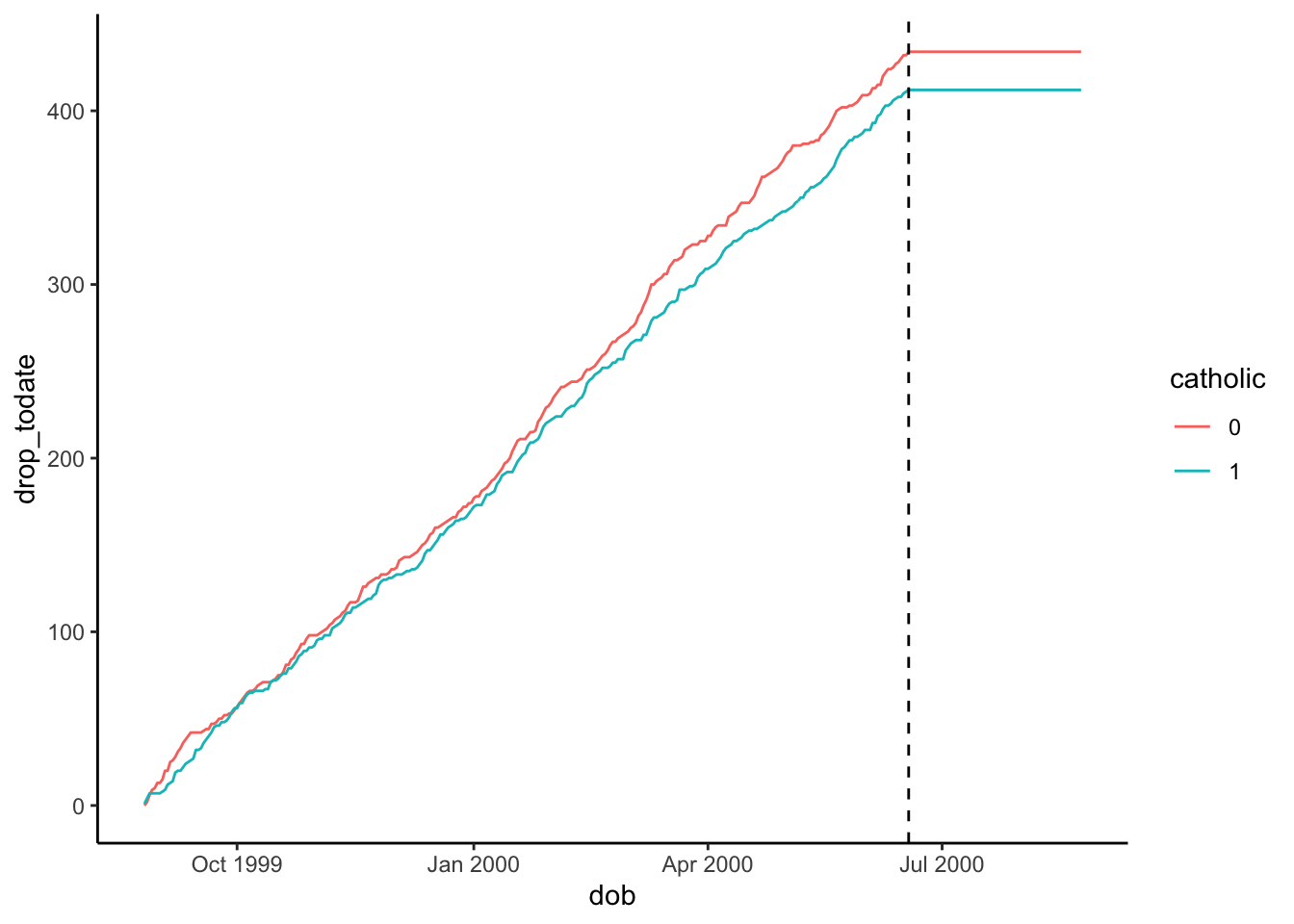
Plot Cumulative Dropouts by Day
Code
|> ggplot (aes (x= dob, y= drop_todate, color= catholic)) + geom_line (linewidth= 0.5 ) + geom_vline (xintercept= lubridate:: make_date (2000 , 6 , 18 ),linetype= 'dashed' ,+ theme_classic ()
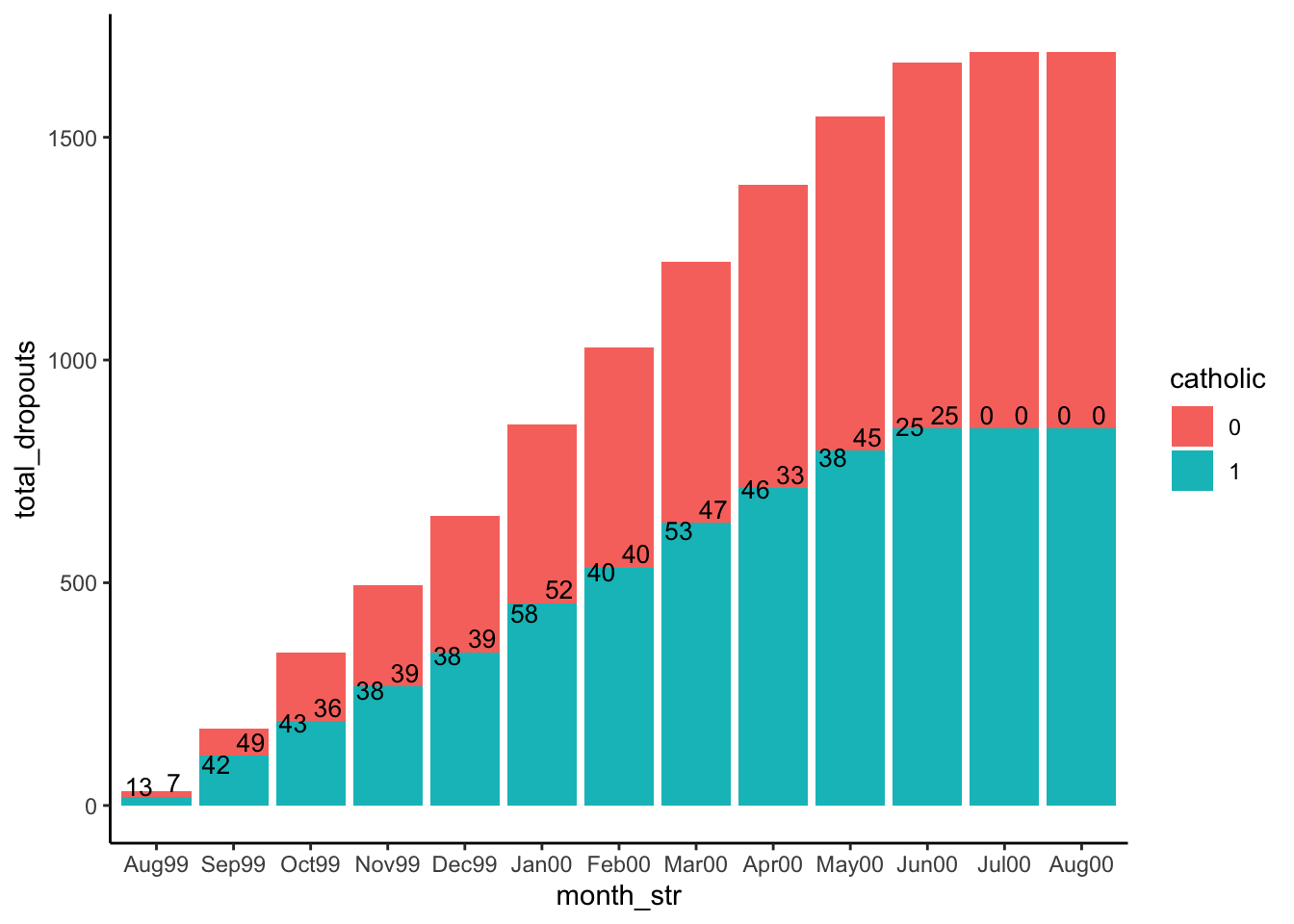
Plot Cumulative Dropouts by Month
Code
<- dob_df |> mutate (year_abbr = as.character (lubridate:: year (dob)),month_str = factor (paste0 ("" ,month.abb[lubridate:: month (dob)],"" ,str_sub (year_abbr, 3 , 4 )),levels= c ("Aug99" ,"Sep99" ,"Oct99" ,"Nov99" ,"Dec99" ,"Jan00" ,"Feb00" ,"Mar00" ,"Apr00" ,"May00" ,"Jun00" ,"Jul00" ,"Aug00" <- dob_df |> group_by (month_str, catholic) |> summarize (month_dropout= sum (dob_dropout))
`summarise()` has grouped output by 'month_str'. You can override using the
`.groups` argument.
Code
$ total_dropouts <- cumsum (month_drop_df$ month_dropout)<- month_drop_df |> mutate (next_month = lead (month_str, default= "Aug00" ),prev_month_dropouts = lag (total_dropouts, default= 0 ),change = total_dropouts - prev_month_dropouts# month_drop_df |> ggplot (aes (x= month_str, y= total_dropouts, fill= catholic)) + geom_bar (stat= 'identity' ) + # geom_segment(aes(xend=next_month), linetype="dashed") + geom_text (aes (label= month_dropout),position= position_dodge (width= 0.9 ),vjust= - 0.25 , size= 3.5 , show.legend= FALSE + theme_classic ()
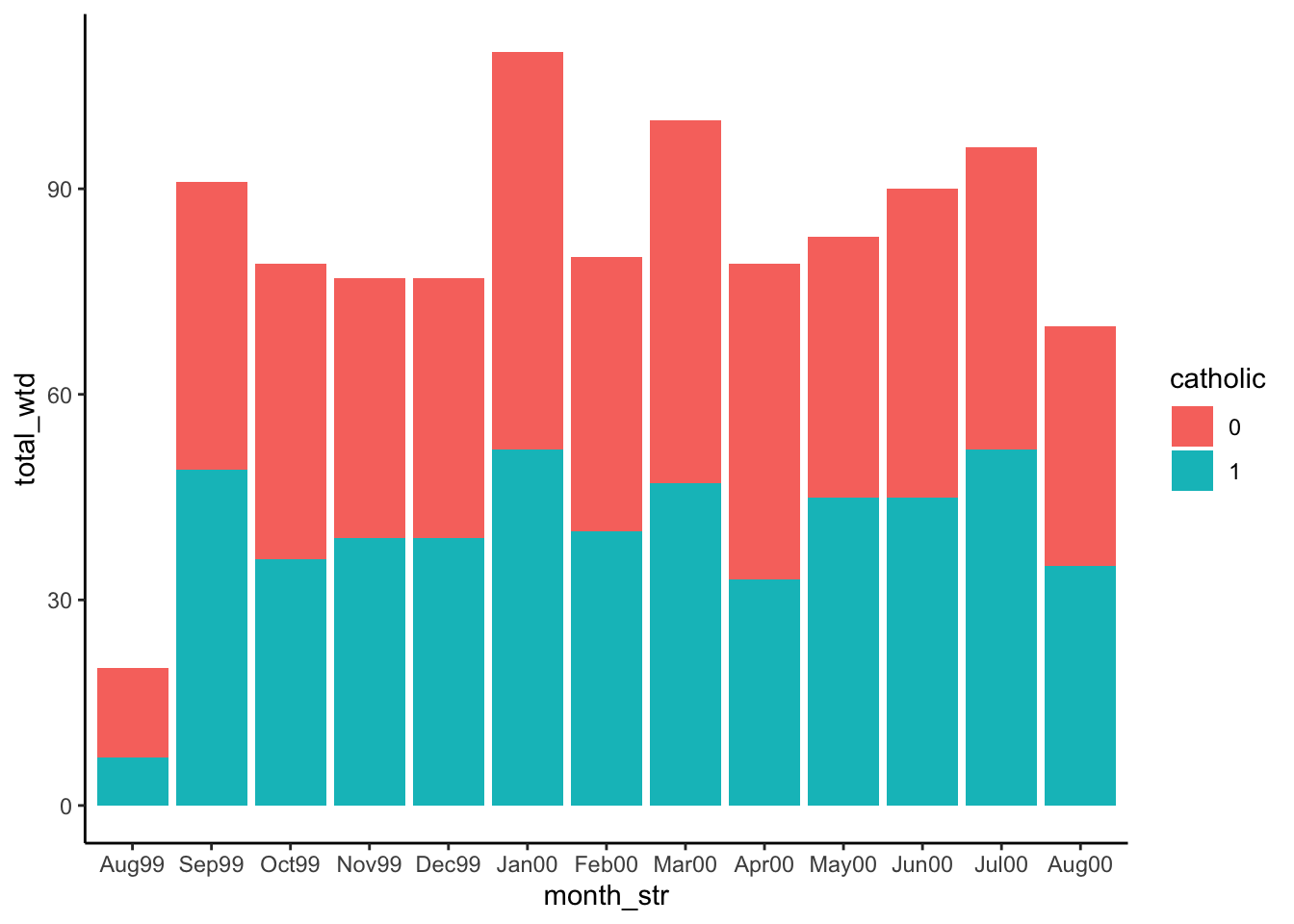
(Sanity check: wtd_df = students who want to drop, per month)
Code
<- student_df |> group_by (month_str, catholic) |> summarize (total_wtd= sum (wants_to_drop))
`summarise()` has grouped output by 'month_str'. You can override using the
`.groups` argument.
Code
|> ggplot (aes (x= month_str, y= total_wtd, fill= catholic)) + geom_bar (stat= 'identity' ) + theme_classic ()
Compute Total Years (with Decimals) of Schooling
Code
<- lubridate:: make_date (2018 , 6 , 18 )<- student_df |> mutate (schooling_start = lubridate:: make_date (2005 , 8 , 26 ),schooling_end = as_date (ifelse (dropout== 1 , as_date (turns_18), as_date (grad_day))),school_days = difftime (schooling_end, schooling_start, units= "days" ),school_yrs = interval (schooling_start, schooling_end) / years (1 )|> head ()
0
0
1999-08-26
2017-08-25
1999
Aug99
1
0
0
2005-08-26
2018-06-18
4679 days
12.81096
0
0
1999-08-26
2017-08-25
1999
Aug99
1
0
0
2005-08-26
2018-06-18
4679 days
12.81096
0
1
1999-08-26
2017-08-25
1999
Aug99
1
0
0
2005-08-26
2018-06-18
4679 days
12.81096
0
1
1999-08-26
2017-08-25
1999
Aug99
1
0
0
2005-08-26
2018-06-18
4679 days
12.81096
0
0
1999-08-26
2017-08-25
1999
Aug99
1
0
0
2005-08-26
2018-06-18
4679 days
12.81096
0
0
1999-08-26
2017-08-25
1999
Aug99
1
0
0
2005-08-26
2018-06-18
4679 days
12.81096
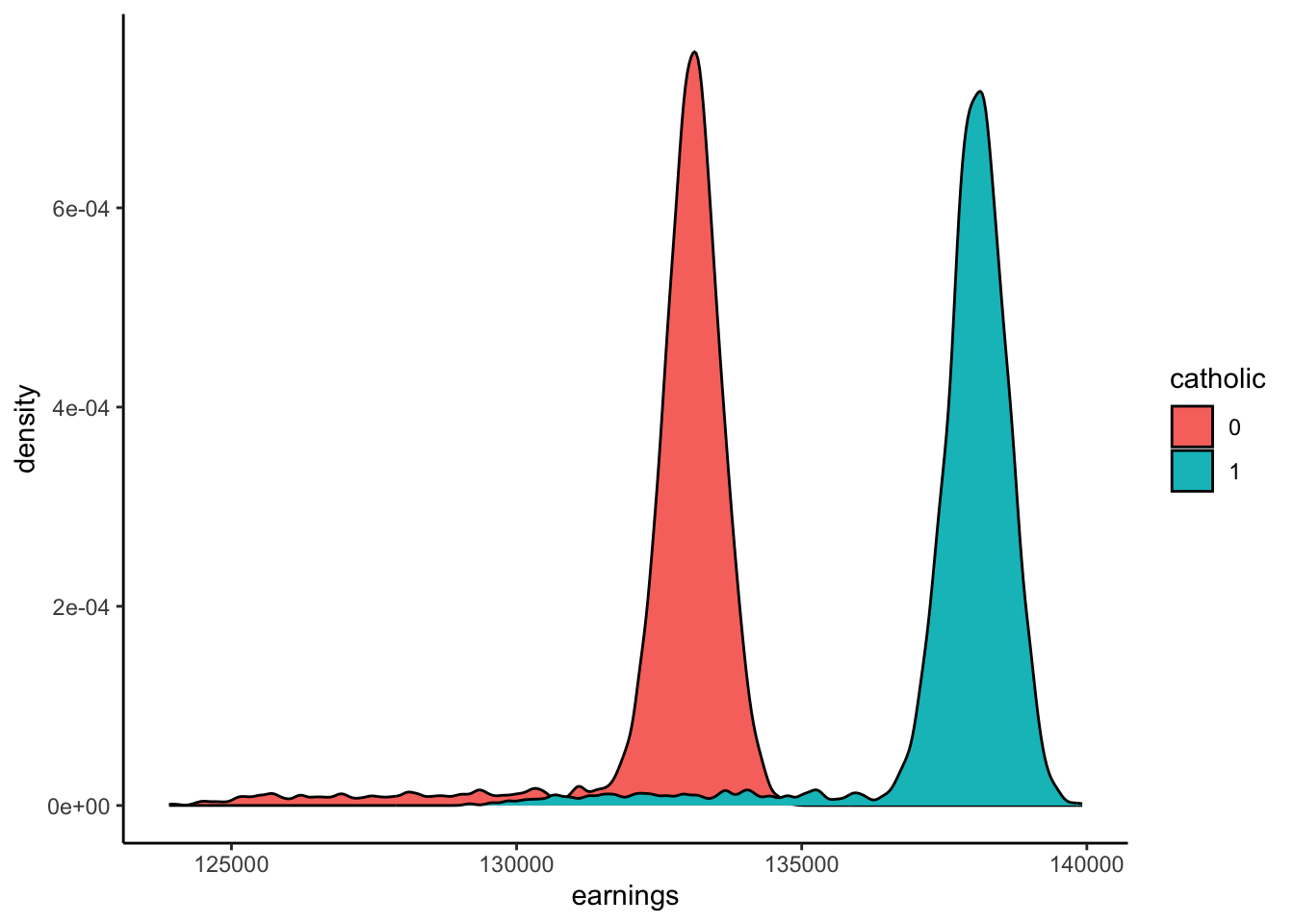
Simulated Earnings \(n\) Years Later
Code
$ earnings_noise <- rnorm (nrow (student_df), 0 , 500 )<- student_df |> mutate (earnings = 10000 * school_yrs + 5000 * as.numeric (catholic) + earnings_noise|> ggplot (aes (x= earnings, fill= catholic)) + geom_density () + theme_classic ()
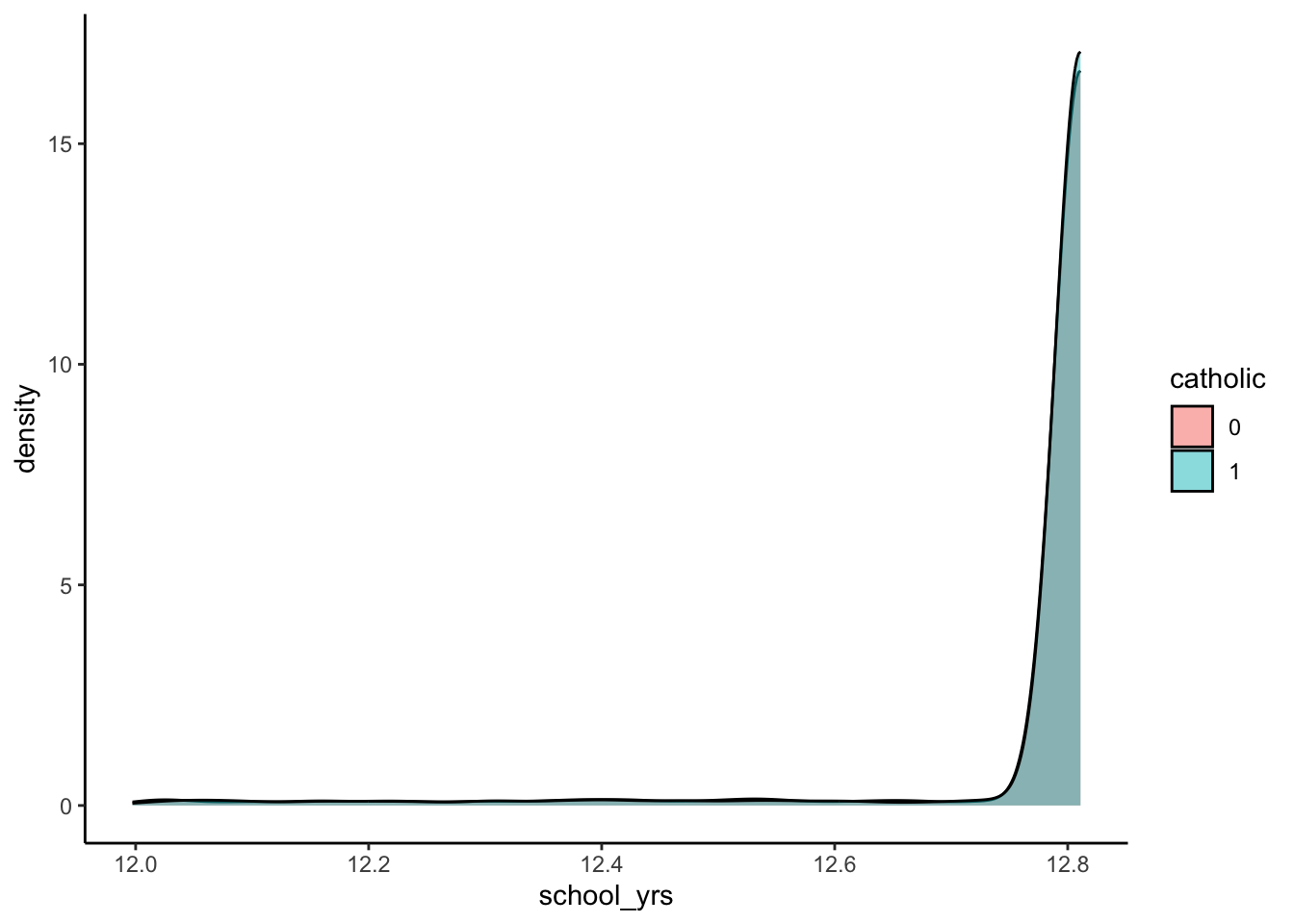
Code
|> ggplot (aes (x= school_yrs, fill= catholic)) + geom_density (alpha= 0.5 ) + theme_classic ()
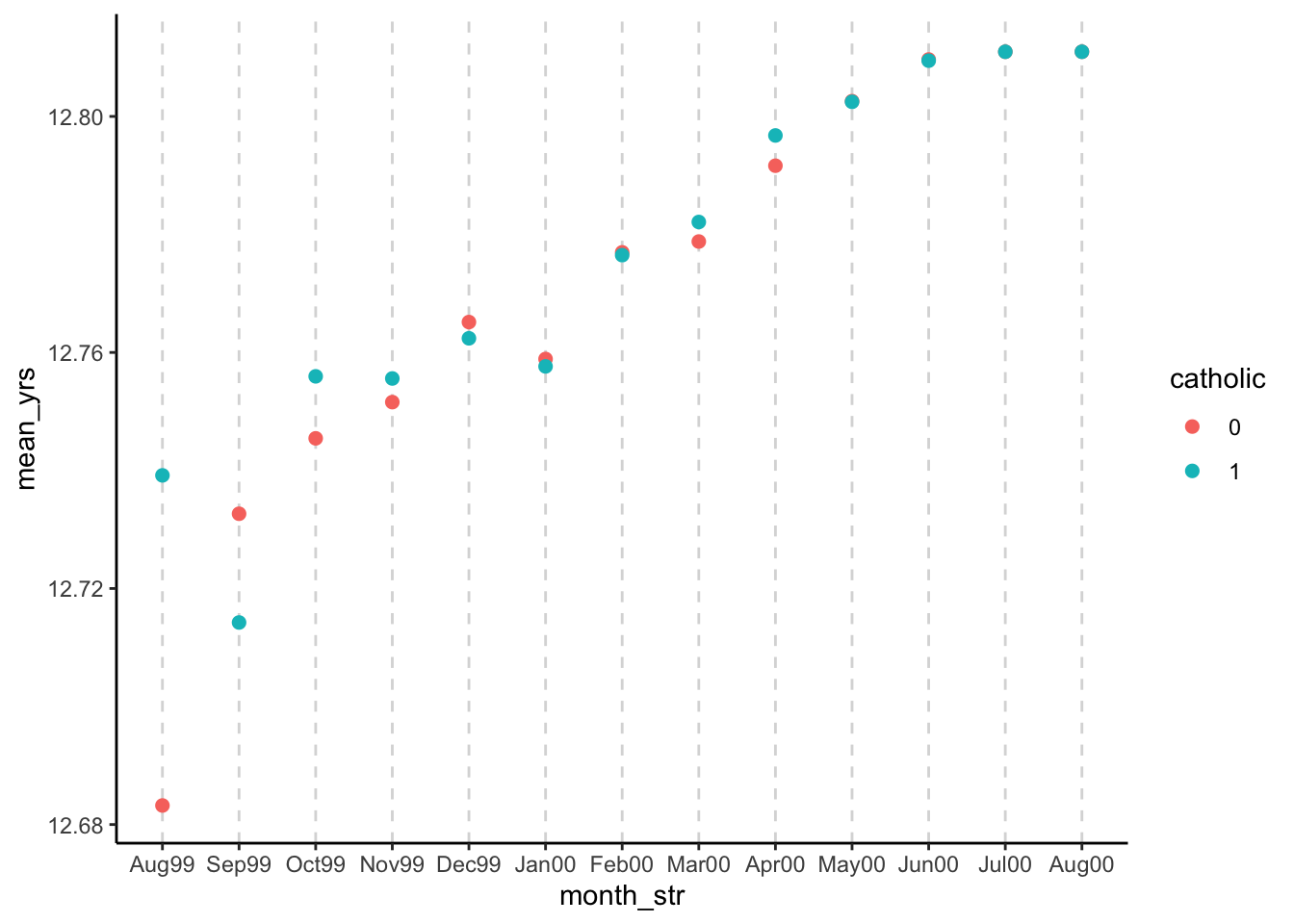
Mean Years of Schooling by Birth Month
Code
<- student_df |> group_by (month_str, catholic) |> summarize (mean_yrs= mean (school_yrs),n= n ()
`summarise()` has grouped output by 'month_str'. You can override using the
`.groups` argument.
Code
# Plot mean school days by month |> ggplot (aes (x= month_str, y= mean_yrs, color= catholic)) + geom_vline (aes (xintercept= month_str), linetype= 'dashed' , linewidth= 0.5 , alpha= 0.18 ) + geom_point (size= 2 ) + theme_classic ()
Code
<- max (student_df$ school_yrs))
Code
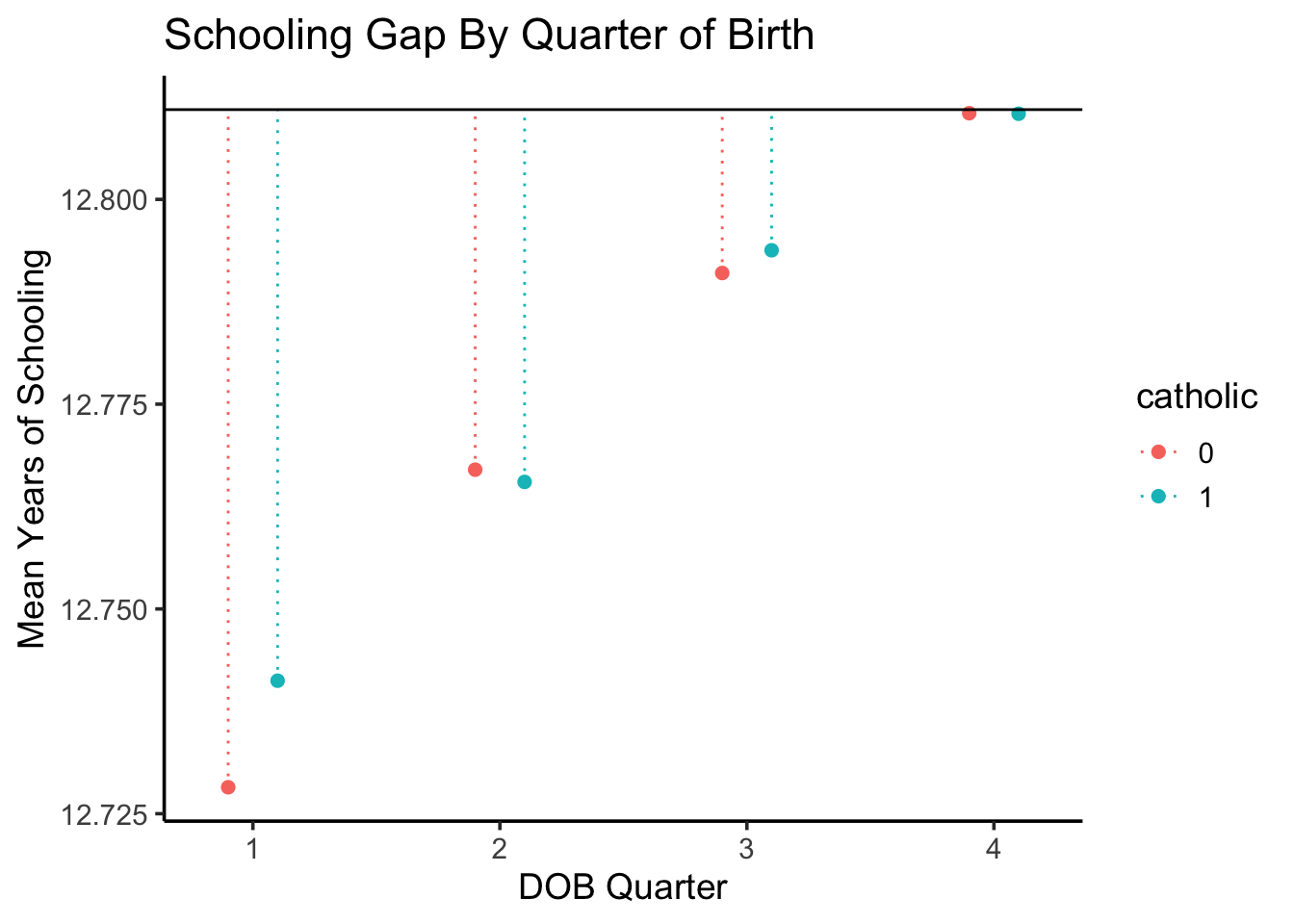
<- c ("Aug99" ,"Sep99" ,"Oct99" ,"Nov99" )<- c ("Dec99" ,"Jan00" ,"Feb00" )<- c ("Mar00" ,"Apr00" ,"May00" )<- c ("Jun00" ,"Jul00" ,"Aug00" )<- schooling_df |> mutate (qtr = case_match (~ 1 ,~ 2 ,~ 3 ,~ 4 <- schooling_df |> group_by (qtr, catholic) |> summarize (mean_yrs_qtr= mean (mean_yrs),n_qtr= sum (n)
`summarise()` has grouped output by 'qtr'. You can override using the `.groups`
argument.
Code
|> ggplot (aes (x= qtr, y= mean_yrs_qtr, color= catholic)) + geom_point (stat= 'identity' , size= 2 , position= position_dodge2 (width= 0.4 )+ geom_segment (aes (yend= max_schooling),# position=position_jitterdodge( # #dodge.width=0.5 # ), position= position_dodge2 (width= 0.4 ),linetype= 'dotted' , linewidth= 0.5 + # ylim(12.759, 12.82) + geom_hline (aes (yintercept= max_schooling,#linetype='Max Possible' linewidth= 0.5 + # scale_linetype_manual("", values=c("dashed")) + # geom_text(x=2.5, y=12.81, label='Maximum Possible (Non-Dropout Amount)', vjust=-1) + labs (title= "Schooling Gap By Quarter of Birth" ,x= "DOB Quarter" ,y= "Mean Years of Schooling" + theme_classic (base_size= 14 )
Code
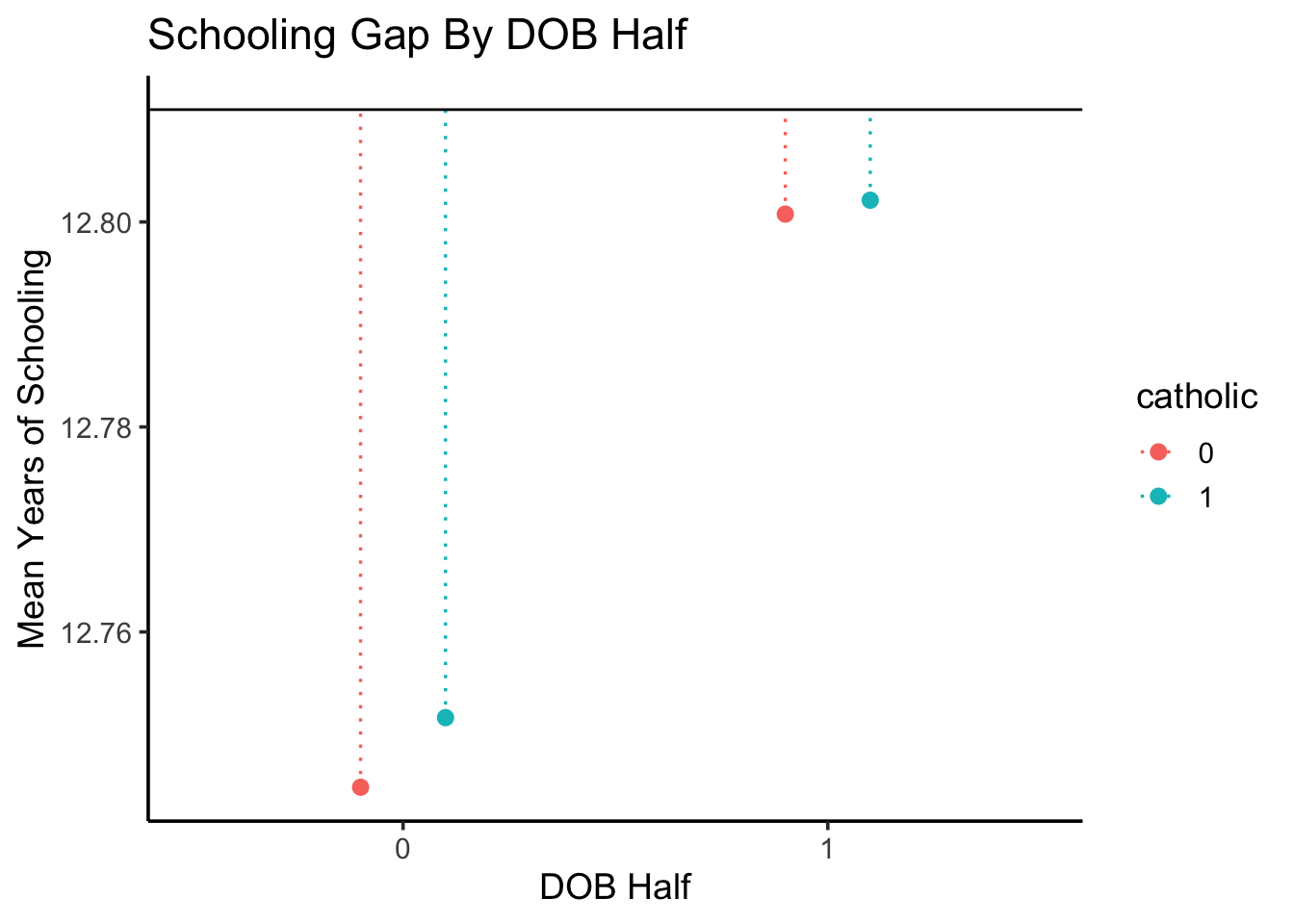
<- schooling_df |> mutate (half = factor (ifelse (qtr== 1 | qtr== 2 , 0 , 1 ),levels= c (0 ,1 )<- schooling_df |> group_by (half, catholic) |> summarize (mean_yrs_half= mean (mean_yrs),n_half= sum (n)
`summarise()` has grouped output by 'half'. You can override using the
`.groups` argument.
Code
|> ggplot (aes (x= half, y= mean_yrs_half, color= catholic)) + geom_point (stat= 'identity' , size= 2.5 ,position= position_dodge2 (width= 0.4 )+ geom_segment (aes (yend= max_schooling),position= position_dodge2 (width= 0.4 ),linetype= 'dotted' , linewidth= 0.6 + # ylim(12.759, 12.82) + geom_hline (aes (yintercept= max_schooling,#linetype='Max Possible' linewidth= 0.5 + # scale_linetype_manual("", values=c("dashed")) + # geom_text(x=1.5, y=12.81, label='Maximum Possible (Non-Dropout Amount)', vjust=-1) + labs (title= "Schooling Gap By DOB Half" ,x= "DOB Half" ,y= "Mean Years of Schooling" + #xlim(0.5, 2.5) + # ylim(12.76, 12.82) + theme_classic (base_size= 14 )
Code
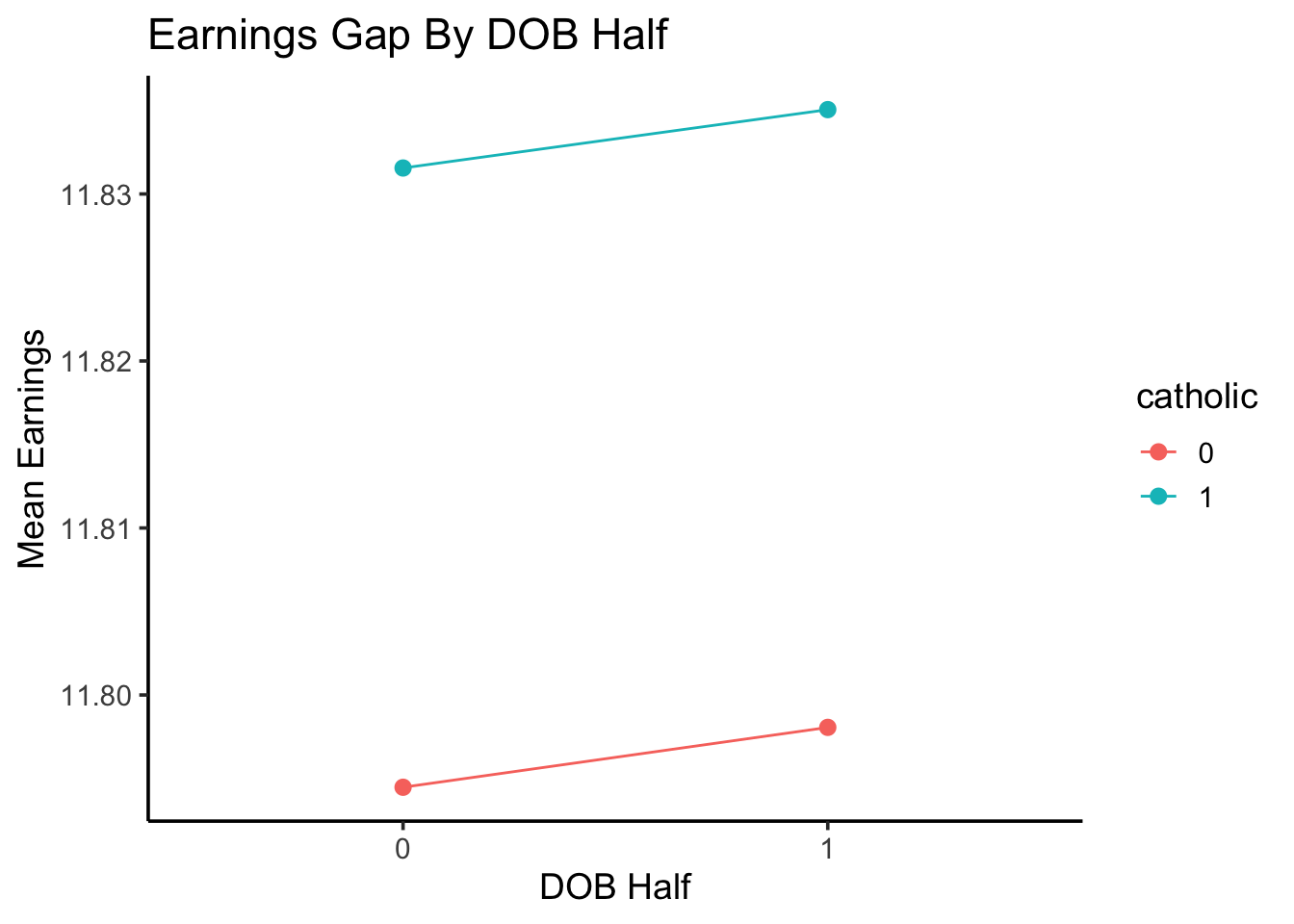
<- c ("Aug99" ,"Sep99" ,"Oct99" ,"Nov99" ,"Dec99" ,"Jan00" ,"Feb00" )<- c ("Mar00" ,"Apr00" ,"May00" ,"Jun00" ,"Jul00" ,"Aug00" )<- student_df |> mutate (half = factor (ifelse (month_str %in% h0, 0 , 1 ),levels= c (0 ,1 )<- student_df |> group_by (half, catholic) |> summarize (mean_earnings= mean (earnings))
`summarise()` has grouped output by 'half'. You can override using the
`.groups` argument.
Code
0
0
132518.2
0
1
137524.1
1
0
132994.3
1
1
138005.8
Code
# earn_df |> pivot_wider(-half) |> ggplot (aes (x= half, y= log (mean_earnings), color= catholic, group= catholic)) + geom_point (stat= 'identity' , size= 2.5 ) + geom_line () + # ylim(12.759, 12.82) + # scale_linetype_manual("", values=c("dashed")) + labs (title= "Earnings Gap By DOB Half" ,x= "DOB Half" ,y= "Mean Earnings" + #xlim(0.5, 2.5) + # ylim(127400, 128100) + theme_classic (base_size= 14 )
Code
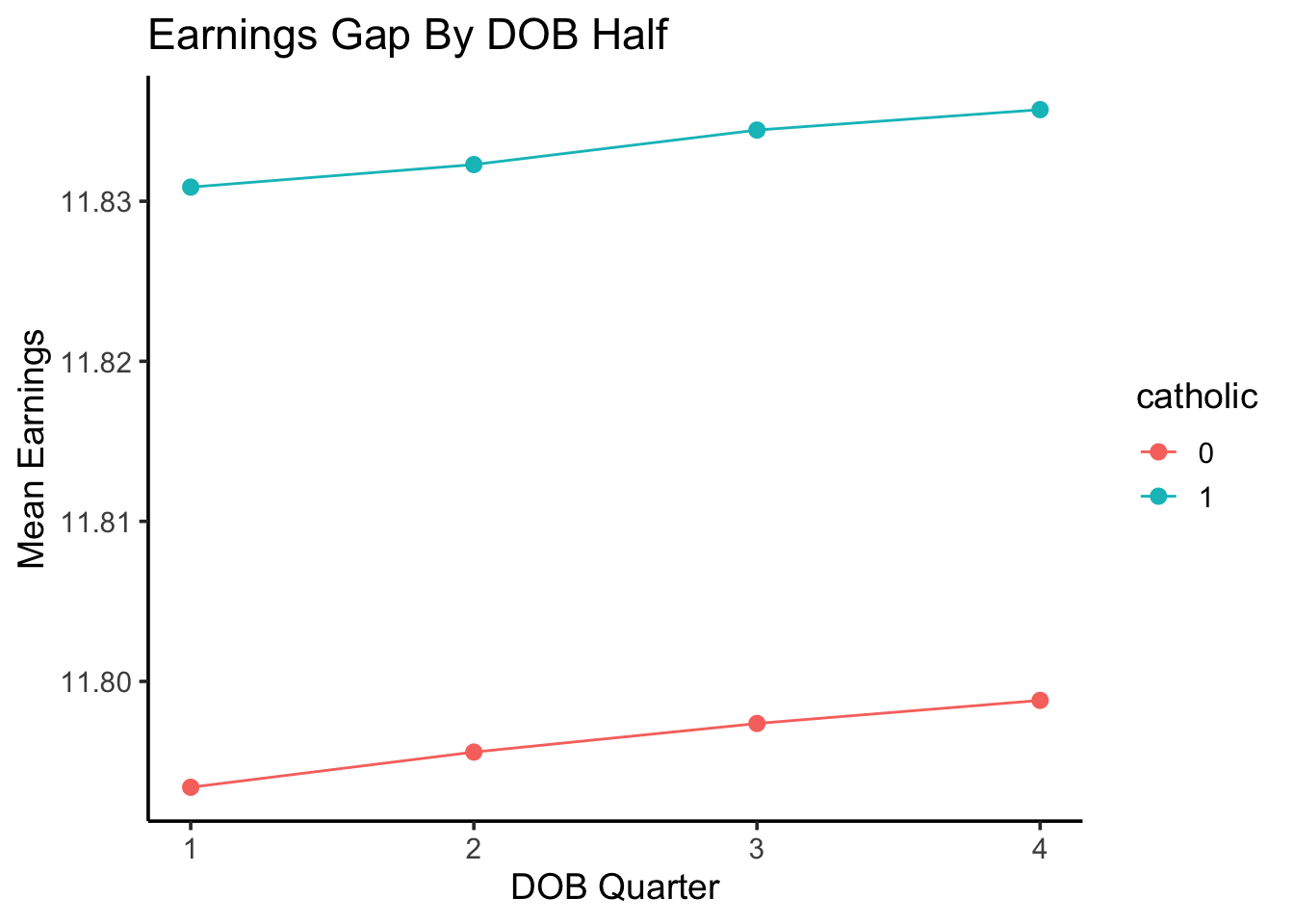
<- student_df |> mutate (qtr = case_match (~ 1 ,~ 2 ,~ 3 ,~ 4 <- student_df |> group_by (qtr, catholic) |> summarize (mean_earnings= mean (earnings))
`summarise()` has grouped output by 'qtr'. You can override using the `.groups`
argument.
Code
1
0
132374.0
1
1
137431.5
2
0
132665.2
2
1
137625.5
3
0
132902.5
3
1
137922.4
4
0
133094.5
4
1
138098.6
Code
# earn_df |> pivot_wider(-half) |> ggplot (aes (x= qtr, y= log (mean_earnings), color= catholic, group= catholic)) + geom_point (stat= 'identity' , size= 2.5 ) + geom_line () + # ylim(12.759, 12.82) + # scale_linetype_manual("", values=c("dashed")) + labs (title= "Earnings Gap By DOB Half" ,x= "DOB Quarter" ,y= "Mean Earnings" + #xlim(0.5, 2.5) + # ylim(127400, 128100) + theme_classic (base_size= 14 )
Code
lm (mean_earnings ~ as.numeric (qtr), data= earn_df)
Call:
lm(formula = mean_earnings ~ as.numeric(qtr), data = earn_df)
Coefficients:
(Intercept) as.numeric(qtr)
134677.1 234.9
Code
lm (as.numeric (catholic) ~ as.numeric (qtr), data= earn_df)
Call:
lm(formula = as.numeric(catholic) ~ as.numeric(qtr), data = earn_df)
Coefficients:
(Intercept) as.numeric(qtr)
1.500e+00 2.402e-16
Code
lm (mean_earnings ~ as.numeric (catholic), data= earn_df)
Call:
lm(formula = mean_earnings ~ as.numeric(catholic), data = earn_df)
Coefficients:
(Intercept) as.numeric(catholic)
127749 5010
References
Angrist, Joshua D., and Alan B. Krueger. 1991.
“Does Compulsory School Attendance Affect Schooling and Earnings ?” The Quarterly Journal of Economics 106 (4): 979–1014.
https://doi.org/10.2307/2937954 .