Week 8: Support Vector Machines
DSAN 5300: Statistical Learning
Spring 2025, Georgetown University
Monday, March 10, 2025
Schedule
Today’s Planned Schedule:
| Start | End | Topic | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lecture | 6:30pm | 7:00pm | Separating Hyperplanes → |
| 7:00pm | 7:20pm | Max-Margin Classifiers → | |
| 7:20pm | 8:00pm | Support Vector Classifiers → | |
| Break! | 8:00pm | 8:10pm | |
| 8:10pm | 9:00pm | Support Vector Machines → |
\[ \DeclareMathOperator*{\argmax}{argmax} \DeclareMathOperator*{\argmin}{argmin} \newcommand{\bigexp}[1]{\exp\mkern-4mu\left[ #1 \right]} \newcommand{\bigexpect}[1]{\mathbb{E}\mkern-4mu \left[ #1 \right]} \newcommand{\definedas}{\overset{\small\text{def}}{=}} \newcommand{\definedalign}{\overset{\phantom{\text{defn}}}{=}} \newcommand{\eqeventual}{\overset{\text{eventually}}{=}} \newcommand{\Err}{\text{Err}} \newcommand{\expect}[1]{\mathbb{E}[#1]} \newcommand{\expectsq}[1]{\mathbb{E}^2[#1]} \newcommand{\fw}[1]{\texttt{#1}} \newcommand{\given}{\mid} \newcommand{\green}[1]{\color{green}{#1}} \newcommand{\heads}{\outcome{heads}} \newcommand{\iid}{\overset{\text{\small{iid}}}{\sim}} \newcommand{\lik}{\mathcal{L}} \newcommand{\loglik}{\ell} \DeclareMathOperator*{\maximize}{maximize} \DeclareMathOperator*{\minimize}{minimize} \newcommand{\mle}{\textsf{ML}} \newcommand{\nimplies}{\;\not\!\!\!\!\implies} \newcommand{\orange}[1]{\color{orange}{#1}} \newcommand{\outcome}[1]{\textsf{#1}} \newcommand{\param}[1]{{\color{purple} #1}} \newcommand{\pgsamplespace}{\{\green{1},\green{2},\green{3},\purp{4},\purp{5},\purp{6}\}} \newcommand{\prob}[1]{P\left( #1 \right)} \newcommand{\purp}[1]{\color{purple}{#1}} \newcommand{\sign}{\text{Sign}} \newcommand{\spacecap}{\; \cap \;} \newcommand{\spacewedge}{\; \wedge \;} \newcommand{\tails}{\outcome{tails}} \newcommand{\Var}[1]{\text{Var}[#1]} \newcommand{\bigVar}[1]{\text{Var}\mkern-4mu \left[ #1 \right]} \]
Quick Roadmap
- Weeks 1-7: Regression was central motivating problem
- (Even when we looked at classification via Logistic Regression, it was regression and then a final thresholding step on the regression result)
- This Week:
- On the one hand, we shift focus to binary classification through learning decision boundaries
- On the other hand, everything we’ve discussed about handling non-linearity will come into play!
Decision Boundaries \(\leadsto\) Max-Margin Classifiers
- Most important building block for SVMs…
- But should not be used on its own! For reasons we’ll see shortly
- (Like “Linear Probability Models” or “Quadratic Splines”, MMCs highlight problem that [usable method] solves!)
- MMC \(\leadsto\) Support Vector Classifiers (can be used)
- MMC \(\leadsto\) Support Vector Machines (can be used)
Learning Decision Boundaries
- How can we get our computer to “learn” which houses I like?
Code
library(tidyverse) |> suppressPackageStartupMessages()
house_df <- tibble::tribble(
~sqm, ~yrs, ~Rating,
10, 5, "Disliked",
10, 20, "Disliked",
20, 22, "Liked",
25, 12, "Liked",
11, 15, "Disliked",
22.1, 5, "Liked"
) |> mutate(
label = ifelse(Rating == "Liked", 1, -1)
)
base_plot <- house_df |> ggplot(aes(x=sqm, y=yrs)) +
labs(
title = "Jeff's House Search",
x = "Square Meters",
y = "Years Old"
) +
expand_limits(x=c(0,25), y=c(0,25)) +
coord_equal() +
# 45 is minus sign, 95 is em-dash
scale_shape_manual(values=c(95, 43)) +
theme_dsan(base_size=14)
base_plot +
geom_point(
aes(color=Rating, shape=Rating), size=g_pointsize * 0.9,
stroke=6
) +
geom_point(aes(fill=Rating), color='black', shape=21, size=6, stroke=0.75, alpha=0.333)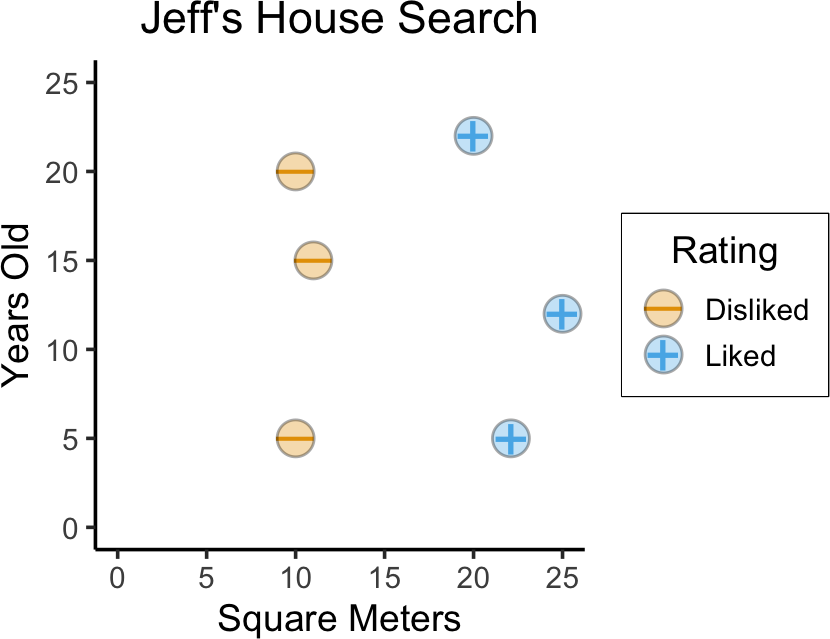
- Naïve idea: Try random lines (each forming a decision boundary), pick “best” one
Code
set.seed(5300)
is_separating <- function(beta_vec) {
beta_str <- paste0(beta_vec, collapse=",")
# print(paste0("is_separating: ",beta_str))
margins <- c()
for (i in 1:nrow(house_df)) {
cur_data <- house_df[i,]
# print(cur_data)
linear_comb <- beta_vec[1] + beta_vec[2] * cur_data$sqm + beta_vec[3] * cur_data$yrs
cur_margin <- cur_data$label * linear_comb
# print(cur_margin)
margins <- c(margins, cur_margin)
}
#print(margins)
return(all(margins > 0) | all(margins < 0))
}
cust_rand_lines_df <- tribble(
~b0, ~b1, ~b2,
# 41, -0.025, -1,
165, -8, -1,
-980, 62, -1
) |> mutate(
slope=-(b1/b2),
intercept=-(b0/b2)
)
num_lines <- 20
rand_b0 <- runif(num_lines, min=-40, max=40)
rand_b1 <- runif(num_lines, min=-2, max=2)
# rand_b2 <- -1 + 2*rbernoulli(num_lines)
rand_b2 <- -1
rand_lines_df <- tibble::tibble(
id=1:num_lines,
b0=rand_b0,
b1=rand_b1,
b2=rand_b2
) |> mutate(
slope=-(b1/b2),
intercept=-(b0/b2)
)
rand_lines_df <- bind_rows(rand_lines_df, cust_rand_lines_df)
# Old school for loop
for (i in 1:nrow(rand_lines_df)) {
cur_line <- rand_lines_df[i,]
cur_beta_vec <- c(cur_line$b0, cur_line$b1, cur_line$b2)
cur_is_sep <- is_separating(cur_beta_vec)
rand_lines_df[i, "is_sep"] <- cur_is_sep
}
base_plot +
geom_abline(
data=rand_lines_df, aes(slope=slope, intercept=intercept), linetype="dashed"
) +
geom_point(
aes(color=Rating, shape=Rating), size=g_pointsize * 0.9,
stroke=6
) +
geom_point(aes(fill=Rating), color='black', shape=21, size=6, stroke=0.75, alpha=0.333) +
labs(
title = paste0("10 Boundary Guesses"),
x = "Square Meters",
y = "Years Old"
)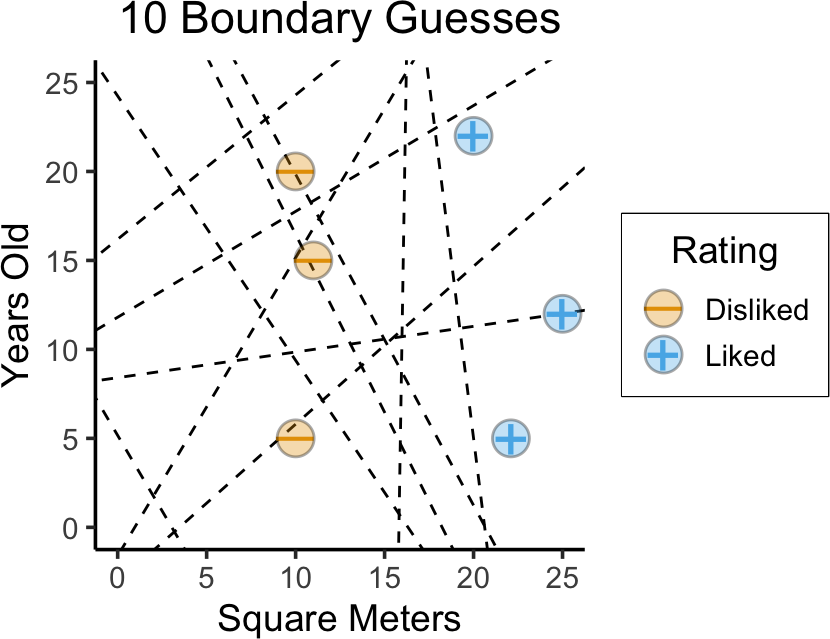
(…Which one is “best”?)
Separating Hyperplanes
- Any line which perfectly separates positive from negative cases is a separating hyperplane
Code
base_plot +
geom_abline(
data=rand_lines_df, aes(slope=slope, intercept=intercept, linetype=is_sep)
) +
geom_abline(
data=rand_lines_df |> filter(is_sep),
aes(slope=slope, intercept=intercept),
linewidth=3, color=cb_palette[4], alpha=0.333
) +
scale_linetype_manual("Separating?", values=c("dotted", "dashed")) +
geom_point(
aes(color=Rating, shape=Rating), size=g_pointsize * 0.9,
stroke=6
) +
geom_point(aes(fill=Rating), color='black', shape=21, size=6, stroke=0.75, alpha=0.333) +
labs(
title = paste0("The Like vs. Dislike Boundary: 10 Guesses"),
x = "Square Meters",
y = "Years Old"
)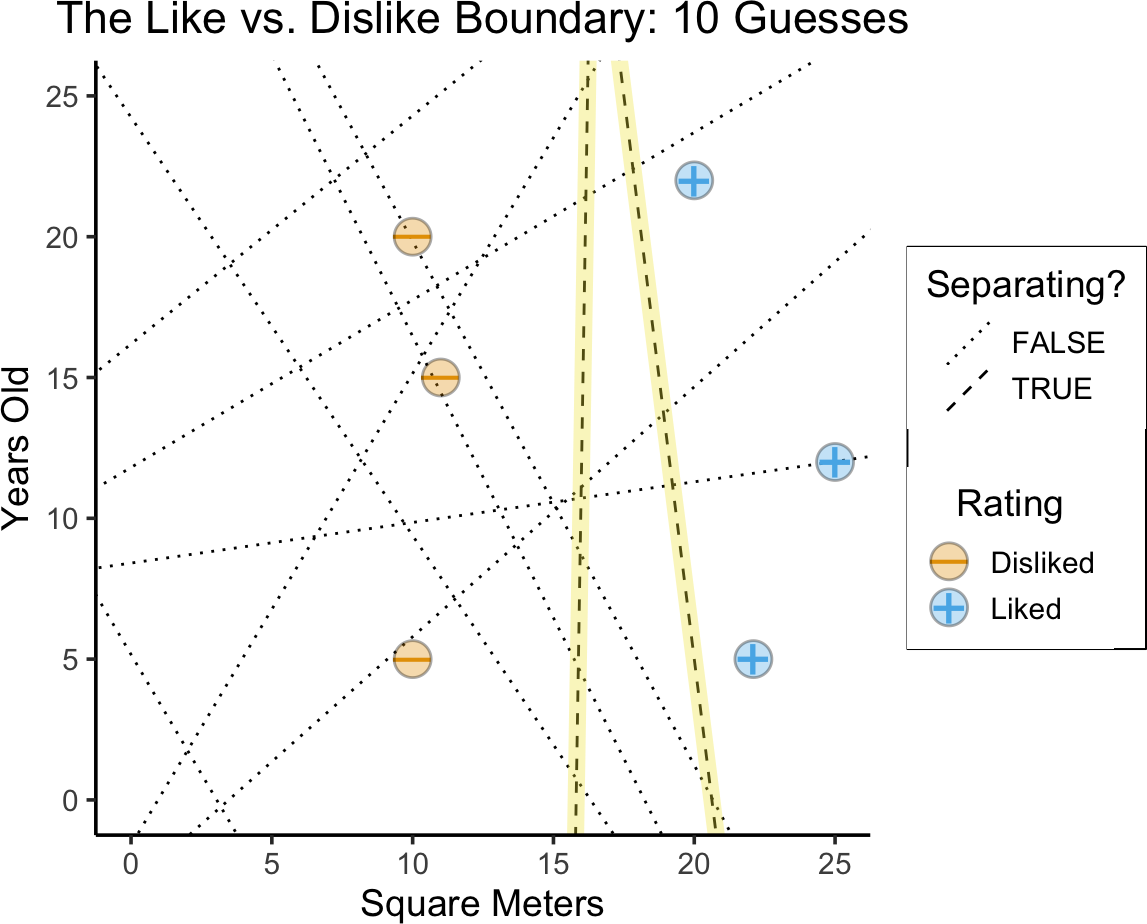
- Why might the left line be better? (Think of DGP!)
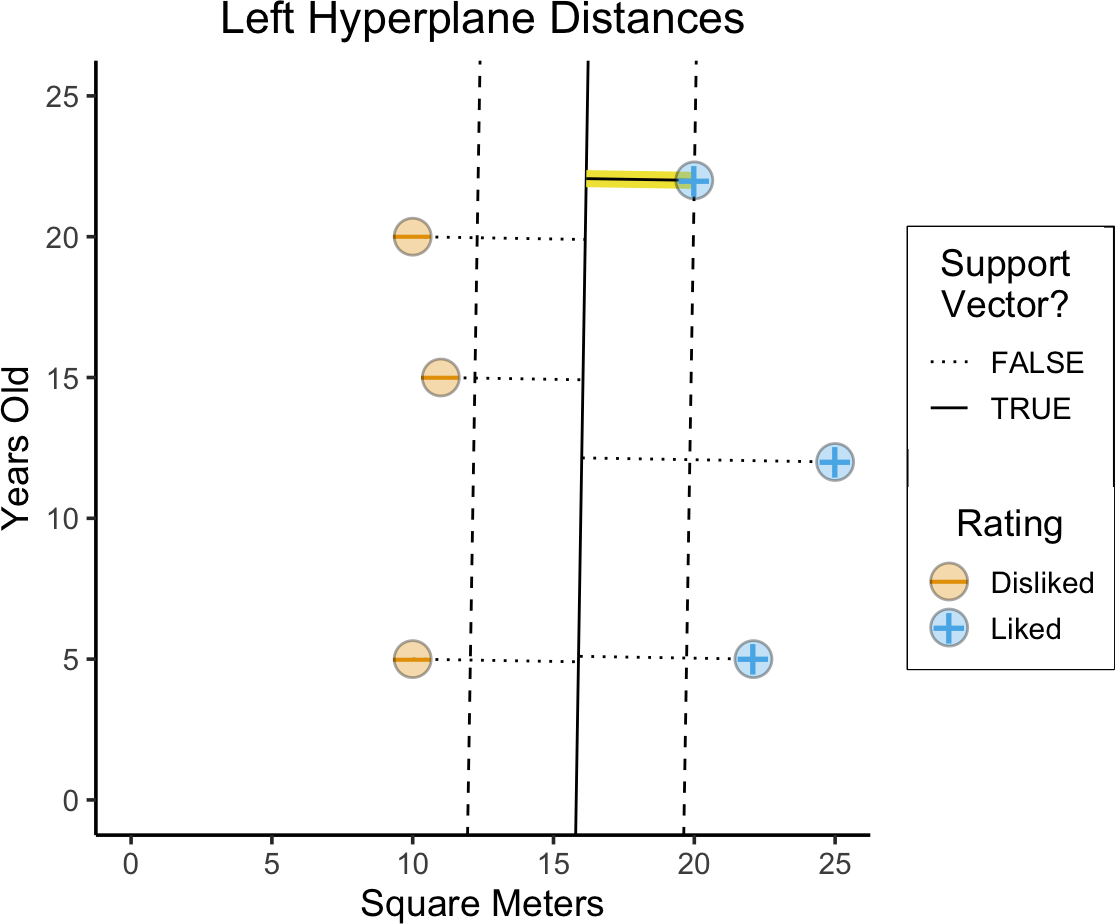
Max-Margin Hyperplanes
- Among the two, left hyperplane establishes a larger margin between the two classes!
- Margin (of hyperplane) = Smallest distance to datapoint (Think of hyperplane as middle of separating slab: how wide is the slab?)
- Important: Note how margin is not the same as average distance!
Code
sep_lines_df <- rand_lines_df |> filter(is_sep) |> mutate(
norm_slope = (-1)/slope
)
cur_line_df <- sep_lines_df |> filter(slope > 0)
# left_line_df
# And make one copy per point
cur_sup_df <- uncount(cur_line_df, nrow(house_df))
cur_sup_df <- bind_cols(cur_sup_df, house_df)
cur_sup_df <- cur_sup_df |> mutate(
norm_intercept = yrs - norm_slope * sqm,
margin_intercept = yrs - slope * sqm,
margin_intercept_gap = intercept - margin_intercept,
margin_intercept_inv = intercept + margin_intercept_gap,
norm_cross_x = -(norm_intercept - intercept) / (norm_slope - slope),
x_gap = norm_cross_x - sqm,
norm_cross_y = yrs + x_gap * norm_slope,
vec_margin = label * (b0 + b1 * sqm + b2 * yrs),
is_sv = vec_margin <= 240
)
base_plot +
geom_abline(
data=cur_line_df, aes(slope=slope, intercept=intercept), linetype="solid"
) +
geom_abline(
data=cur_sup_df |> filter(is_sv),
aes(
slope=slope,
intercept=margin_intercept
),
linetype="dashed"
) +
geom_abline(
data=cur_sup_df |> filter(is_sv),
aes(
slope=slope,
intercept=margin_intercept_inv
),
linetype="dashed"
) +
geom_segment(
data=cur_sup_df |> filter(is_sv),
aes(x=sqm, y=yrs, xend=norm_cross_x, yend=norm_cross_y),
color=cb_palette[4], linewidth=3
) +
geom_segment(
data=cur_sup_df,
aes(x=sqm, y=yrs, xend=norm_cross_x, yend=norm_cross_y, linetype=is_sv)
) +
geom_point(
aes(color=Rating, shape=Rating), size=g_pointsize * 0.9,
stroke=6
) +
geom_point(aes(fill=Rating), color='black', shape=21, size=6, stroke=0.75, alpha=0.333) +
scale_linetype_manual("Support\nVector?", values=c("dotted", "solid")) +
labs(
title = paste0("Left Hyperplane Distances"),
x = "Square Meters",
y = "Years Old"
)
Code
# New calculation: line with same slope but that hits the SV
# y - y1 = m(x - x1), so...
# y - yrs = m(x - sqm) <=> y = m(x-sqm) + yrs <=> y = mx - m*sqm + yrs
# <=> b = yrs - -m*sqm
cur_line_df <- sep_lines_df |> filter(slope < 0)
# left_line_df
# And make one copy per point
cur_sup_df <- uncount(cur_line_df, nrow(house_df))
cur_sup_df <- bind_cols(cur_sup_df, house_df)
cur_sup_df <- cur_sup_df |> mutate(
norm_intercept = yrs - norm_slope * sqm,
margin_intercept = yrs - slope * sqm,
margin_intercept_gap = intercept - margin_intercept,
margin_intercept_inv = intercept + margin_intercept_gap,
norm_cross_x = -(norm_intercept - intercept) / (norm_slope - slope),
x_gap = norm_cross_x - sqm,
norm_cross_y = yrs + x_gap * norm_slope,
vec_margin = abs(label * (b0 + b1 * sqm + b2 * yrs)),
is_sv = vec_margin <= 25
)
base_plot +
geom_abline(
data=cur_line_df, aes(slope=slope, intercept=intercept), linetype="solid"
) +
geom_abline(
data=cur_sup_df |> filter(is_sv),
aes(
slope=slope,
intercept=margin_intercept
),
linetype="dashed"
) +
geom_abline(
data=cur_sup_df |> filter(is_sv),
aes(
slope=slope,
intercept=margin_intercept_inv
),
linetype="dashed"
) +
# geom_abline(
# data=cur_line_df,
# aes(slope=slope, intercept=intercept),
# linewidth=3, color=cb_palette[4], alpha=0.333
# ) +
geom_segment(
data=cur_sup_df |> filter(vec_margin <= 18),
aes(x=sqm, y=yrs, xend=norm_cross_x, yend=norm_cross_y),
color=cb_palette[4], linewidth=3
) +
geom_segment(
data=cur_sup_df,
aes(x=sqm, y=yrs, xend=norm_cross_x, yend=norm_cross_y, linetype=is_sv)
) +
geom_point(
aes(color=Rating, shape=Rating), size=g_pointsize * 0.9,
stroke=6
) +
geom_point(aes(fill=Rating), color='black', shape=21, size=6, stroke=0.75, alpha=0.333) +
scale_linetype_manual("Support\nVector?", values=c("dotted", "solid")) +
labs(
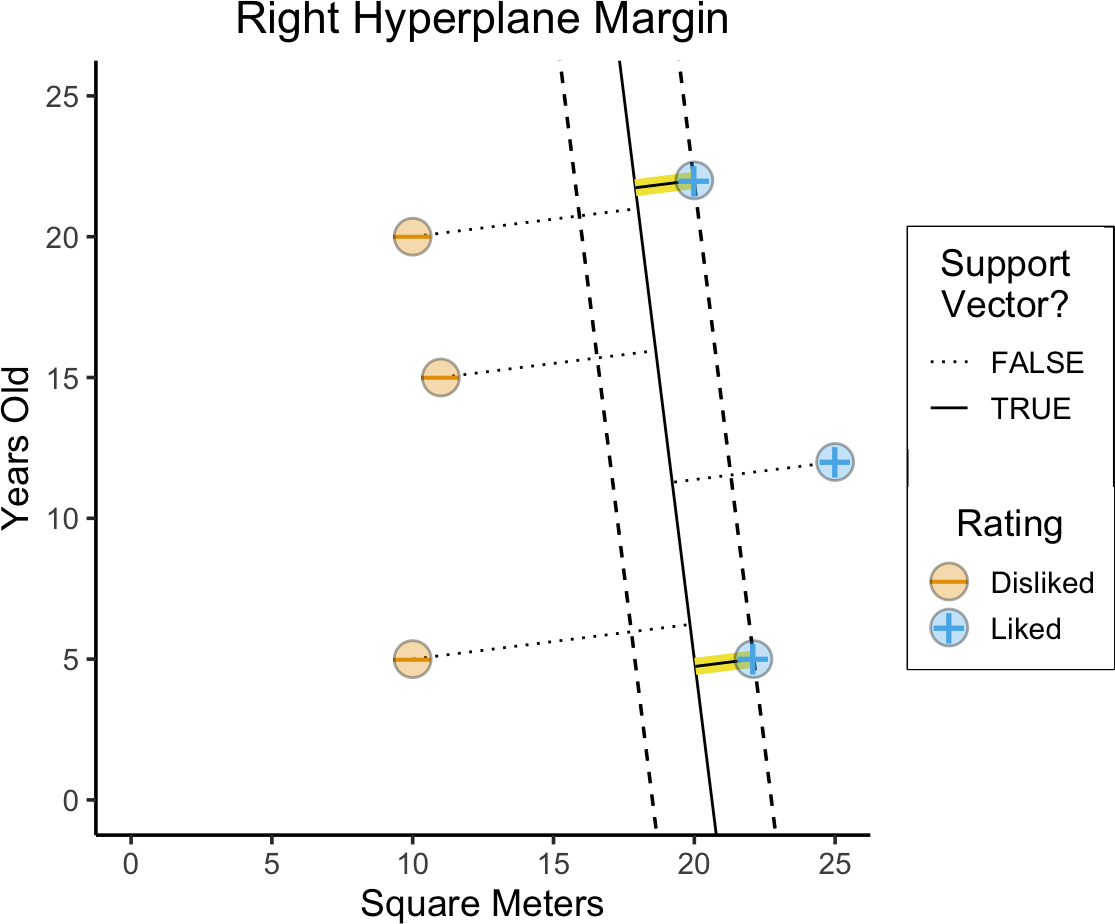
title = paste0("Right Hyperplane Margin"),
x = "Square Meters",
y = "Years Old"
)
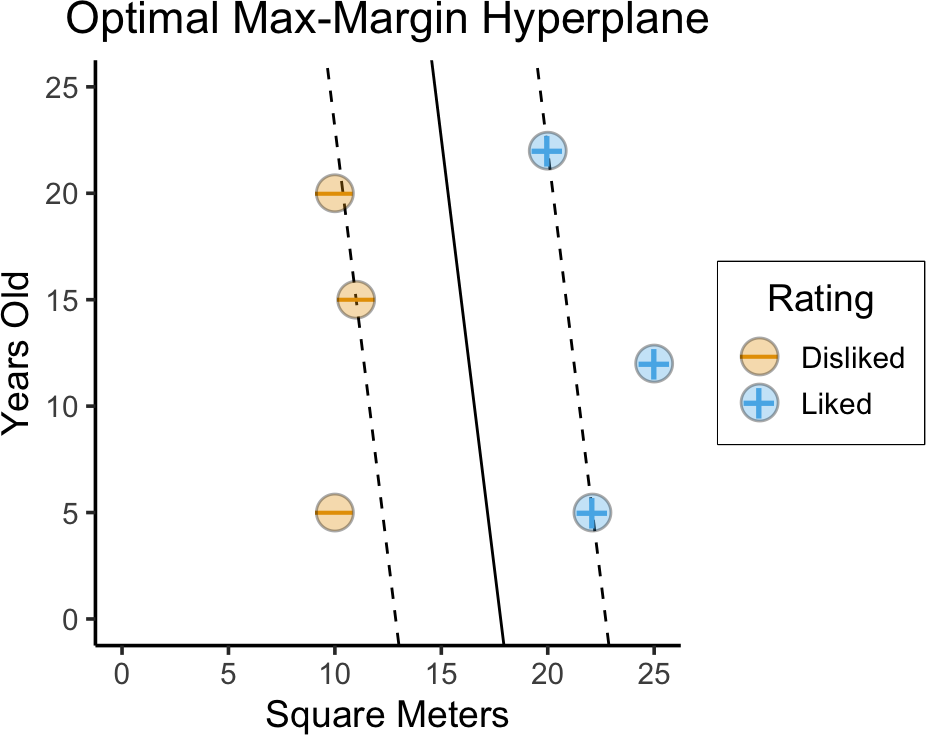
Optimal Max-Margin Hyperplane
- On previous slides we chose from a small set of randomly-generated lines…
- Now that we have max-margin objective, we can optimize over all possible lines!
- Any hyperplane can be written as \(\beta_0 + \beta_1 x_{1} + \beta_2 x_{2} = 0\)
Let \(y_i = \begin{cases} +1 &\text{if house }i\text{ Liked} \\ -1 &\text{if house }i\text{ Disliked}\end{cases}\)
\[ \begin{align*} \underset{\beta_0, \beta_1, \beta_2, M}{\text{maximize}}\text{ } & M \\ \text{s.t. } & y_i(\beta_0 + \beta_1 x_{i1} + \beta_2 x_{i2}) \geq M, \\ ~ & \beta_0^2 + \beta_1^2 + \beta_2^2 = 1 \end{align*} \]
- \(\beta_0^2 + \beta_1^2 + \beta_2^2 = 1\) just ensures that \(y_i(\beta_0 + \beta_1 x_{i1} + \beta_2 x_{i2})\) gives distance from hyperplane to \(x_i\)
Code
library(e1071)
liked <- as.factor(house_df$Rating == "Liked")
cent_df <- house_df
cent_df$sqm <- scale(cent_df$sqm)
cent_df$yrs <- scale(cent_df$yrs)
svm_model <- svm(liked ~ sqm + yrs, data=cent_df, kernel="linear")
cf <- coef(svm_model)
sep_intercept <- -cf[1] / cf[3]
sep_slope <- -cf[2] / cf[3]
# Invert Z-scores
sd_ratio <- sd(house_df$yrs) / sd(house_df$sqm)
inv_slope <- sd_ratio * sep_slope
inv_intercept <- mean(house_df$yrs) - inv_slope * mean(house_df$sqm) + sd(house_df$yrs)*sep_intercept
# And the margin boundary
sv_index <- svm_model$index[1]
sv_sqm <- house_df$sqm[sv_index]
sv_yrs <- house_df$yrs[sv_index]
margin_intercept <- sv_yrs - inv_slope * sv_sqm
margin_diff <- inv_intercept - margin_intercept
margin_intercept_inv <- inv_intercept + margin_diff
base_plot +
coord_equal() +
scale_shape_manual(values=c(95, 43)) +
theme_dsan(base_size=14) +
geom_abline(
intercept=inv_intercept, slope=inv_slope, linetype="solid"
) +
geom_abline(
intercept=margin_intercept, slope=inv_slope, linetype="dashed"
) +
geom_abline(
intercept=margin_intercept_inv, slope=inv_slope, linetype="dashed"
) +
geom_point(
aes(color=Rating, shape=Rating), size=g_pointsize * 0.9,
stroke=6
) +
geom_point(aes(fill=Rating), color='black', shape=21, size=6, stroke=0.75, alpha=0.333) +
scale_linetype_manual("Support\nVector?", values=c("dotted", "solid")) +
labs(
title = "Optimal Max-Margin Hyperplane",
x = "Square Meters",
y = "Years Old"
)
When Does This Fail?
- What do we do in this case? (No separating hyperplane!)
Code
# Generate gaussian blob of disliked + gaussian
# blob of liked :3
library(mvtnorm) |> suppressPackageStartupMessages()
set.seed(5304)
num_houses <- 100
# Shared covariance matrix
Sigma_all <- matrix(c(12,0,0,20), nrow=2, ncol=2, byrow=TRUE)
# Negative datapoints
mu_neg <- c(10, 12.5)
neg_matrix <- rmvnorm(num_houses/2, mean=mu_neg, sigma=Sigma_all)
colnames(neg_matrix) <- c("sqm", "yrs")
neg_df <- as_tibble(neg_matrix) |> mutate(Rating="Disliked")
# Positive datapoints
mu_pos <- c(21, 12.5)
pos_matrix <- rmvnorm(num_houses/2, mean=mu_pos, sigma=Sigma_all)
colnames(pos_matrix) <- c("sqm", "yrs")
pos_df <- as_tibble(pos_matrix) |> mutate(Rating="Liked")
# And combine
nonsep_df <- bind_rows(neg_df, pos_df)
nonsep_df <- nonsep_df |> filter(yrs >= 5 & sqm <= 24 & sqm >= 7)
# Plot
nonsep_plot <- nonsep_df |> ggplot(aes(x=sqm, y=yrs)) +
labs(
title = "Jeff's House Search",
x = "Square Meters",
y = "Years Old"
) +
# xlim(6,25) + ylim(2,22) +
coord_equal() +
# 45 is minus sign, 95 is em-dash
scale_shape_manual(values=c(95, 43)) +
theme_dsan(base_size=22)
nonsep_plot +
geom_point(
aes(color=Rating, shape=Rating), size=g_pointsize * 0.25,
stroke=6
) +
geom_point(aes(fill=Rating), color='black', shape=21, size=4, stroke=0.75, alpha=0.333)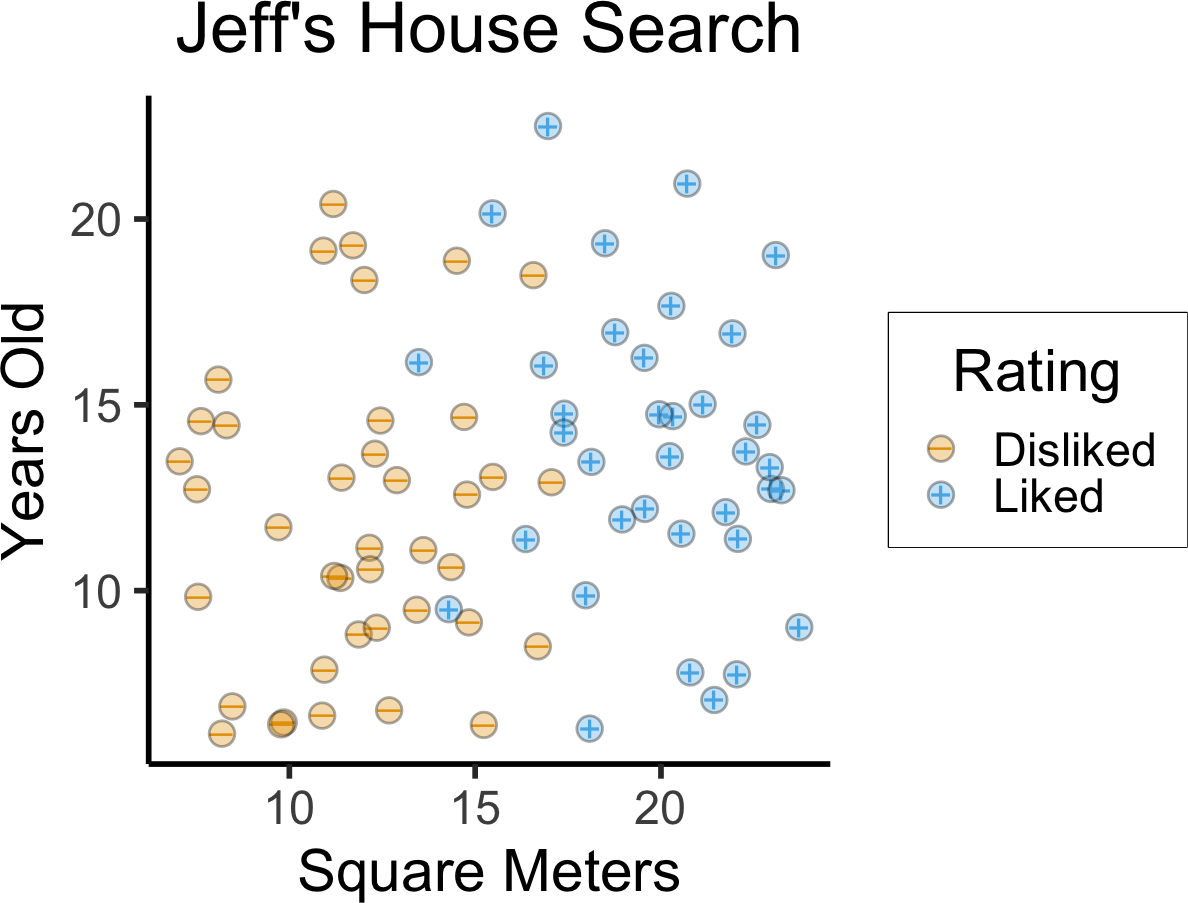
- Here we need to keep in mind how our goal is relative to the Data-Generating Process!
No Separating Hyperplane? 😧

- Don’t let the perfect be the enemy of the good!
Perfect vs. Good
- In fact, “sub-optimal” may be better than optimal, in terms of overfitting!
ISLR Figure 9.5: Notice how the dashed line on the right side may be better in terms of generalization, even though the solid line is the optimal Max-Margin Hyperplane!
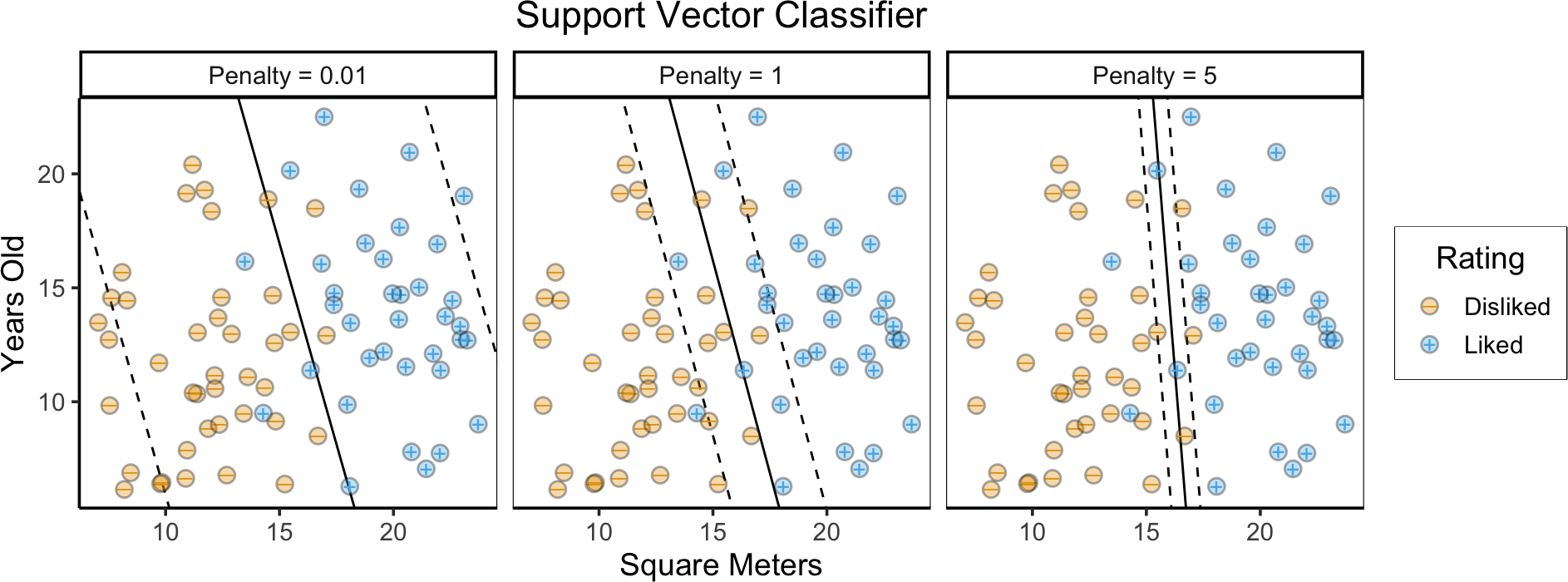
Support Vector Classifiers
- Max-Margin Classifier + budget \(C\) for errors
Handling Non-Linearly-Separable Data
\[ \begin{align*} \underset{\beta_0, \beta_1, \beta_2, \varepsilon_1, \ldots, \varepsilon_n, M}{\text{maximize}}\text{ } \; & M \\ \text{s.t. } \; & y_i(\beta_0 + \beta_1 x_{i1} + \beta_2 x_{i2}) \geq M(1 - \varepsilon_i), \\ ~ & \varepsilon_i \geq 0, \sum_{i=1}^{n}\varepsilon_i \leq C, \\ ~ & \beta_0^2 + \beta_1^2 + \beta_2^2 = 1 \end{align*} \]
- \(C = 0\) \(\implies\) Max-Margin Classifier
- We want to choose \(C\) to optimize generalizability to unseen data… So, choose via Cross-Validation
“Slack” Variables
- The \(\varepsilon_i\) values also give us valuable information!
- \(\varepsilon_i = 0 \implies\) observation \(i\) on correct side of margin
- \(0 < \varepsilon_i \leq 1 \implies\) observation \(i\) is within margin but on correct side of hyperplane
- \(\varepsilon_i > 1 \implies\) observation \(i\) on wrong side of hyperplane
Our Non-Linearly-Separable Example
Code
library(e1071)
liked <- as.factor(nonsep_df$Rating == "Liked")
nonsep_cent_df <- nonsep_df
nonsep_cent_df$sqm <- scale(nonsep_cent_df$sqm)
nonsep_cent_df$yrs <- scale(nonsep_cent_df$yrs)
# Compute boundary for different cost budgets
budget_vals <- c(0.01, 1, 5)
svm_df <- tibble(
sep_slope=numeric(), sep_intercept=numeric(),
inv_slope=numeric(), inv_intercept=numeric(),
margin_intercept=numeric(), margin_intercept_inv=numeric(),
budget=numeric(), budget_label=character()
)
for (cur_c in budget_vals) {
# print(cur_c)
svm_model <- svm(liked ~ sqm + yrs, data=nonsep_cent_df, kernel="linear", cost=cur_c)
cf <- coef(svm_model)
sep_intercept <- -cf[1] / cf[3]
sep_slope <- -cf[2] / cf[3]
# Invert Z-scores
sd_ratio <- sd(nonsep_df$yrs) / sd(nonsep_df$sqm)
inv_slope <- sd_ratio * sep_slope
inv_intercept <- mean(nonsep_df$yrs) - inv_slope * mean(nonsep_df$sqm) + sd(nonsep_df$yrs)*sep_intercept
# And the margin boundary
sv_index <- svm_model$index[1]
sv_sqm <- nonsep_df$sqm[sv_index]
sv_yrs <- nonsep_df$yrs[sv_index]
margin_intercept <- sv_yrs - inv_slope * sv_sqm
margin_diff <- inv_intercept - margin_intercept
margin_intercept_inv <- inv_intercept + margin_diff
cur_svm_row <- tibble_row(
budget = cur_c,
budget_label = paste0("Penalty = ",cur_c),
sep_slope = sep_slope,
sep_intercept = sep_intercept,
inv_slope = inv_slope,
inv_intercept = inv_intercept,
margin_intercept = margin_intercept,
margin_intercept_inv = margin_intercept_inv
)
svm_df <- bind_rows(svm_df, cur_svm_row)
}
ggplot() +
# xlim(6,25) + ylim(2,22) +
coord_equal() +
# 45 is minus sign, 95 is em-dash
scale_shape_manual(values=c(95, 43)) +
theme_dsan(base_size=14) +
geom_abline(
data=svm_df,
aes(intercept=inv_intercept, slope=inv_slope),
linetype="solid"
) +
geom_abline(
data=svm_df,
aes(intercept=margin_intercept, slope=inv_slope),
linetype="dashed"
) +
geom_abline(
data=svm_df,
aes(intercept=margin_intercept_inv, slope=inv_slope),
linetype="dashed"
) +
geom_point(
data=nonsep_df,
aes(x=sqm, y=yrs, color=Rating, shape=Rating), size=g_pointsize * 0.1,
stroke=5
) +
geom_point(
data=nonsep_df,
aes(x=sqm, y=yrs, fill=Rating), color='black', shape=21, size=3, stroke=0.75, alpha=0.333
) +
labs(
title = "Support Vector Classifier",
x = "Square Meters",
y = "Years Old"
) +
facet_wrap(vars(budget_label), nrow=1) +
theme(
panel.border = element_rect(color = "black", fill = NA, size = 0.4)
)
But… Why Restrict Ourselves to Lines?
- We just spent 7 weeks learning how to move from linear to non-linear! Basic template:
\[ \text{Nonlinear model} = \text{Linear model} \underbrace{- \; \text{linearity restriction}}_{\text{Enables overfitting...}} \underbrace{+ \text{ Complexity penalty}}_{\text{Prevent overfitting}} \]
- So… We should be able to find reasonable non-linear boundaries!
From MathWorks
Support Vector Machines
This is where stuff gets super…
Linear
Linear \(\rightarrow\) Linear
- Old feature space: \(\mathcal{S} = \{X_1, \ldots, X_J\}\)
- New feature space: \(\mathcal{S}^2 = \{X_1, X_1^2, \ldots, X_J, X_J^2\}\)
- Linear boundary in \(\mathcal{S}^2\) \(\implies\) Quadratic boundary in \(\mathcal{S}\)
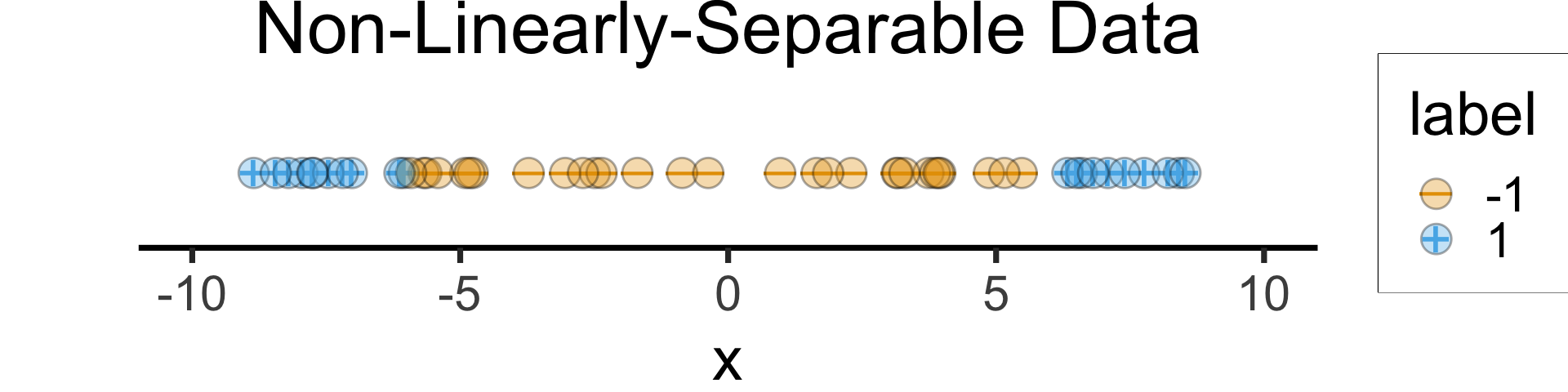
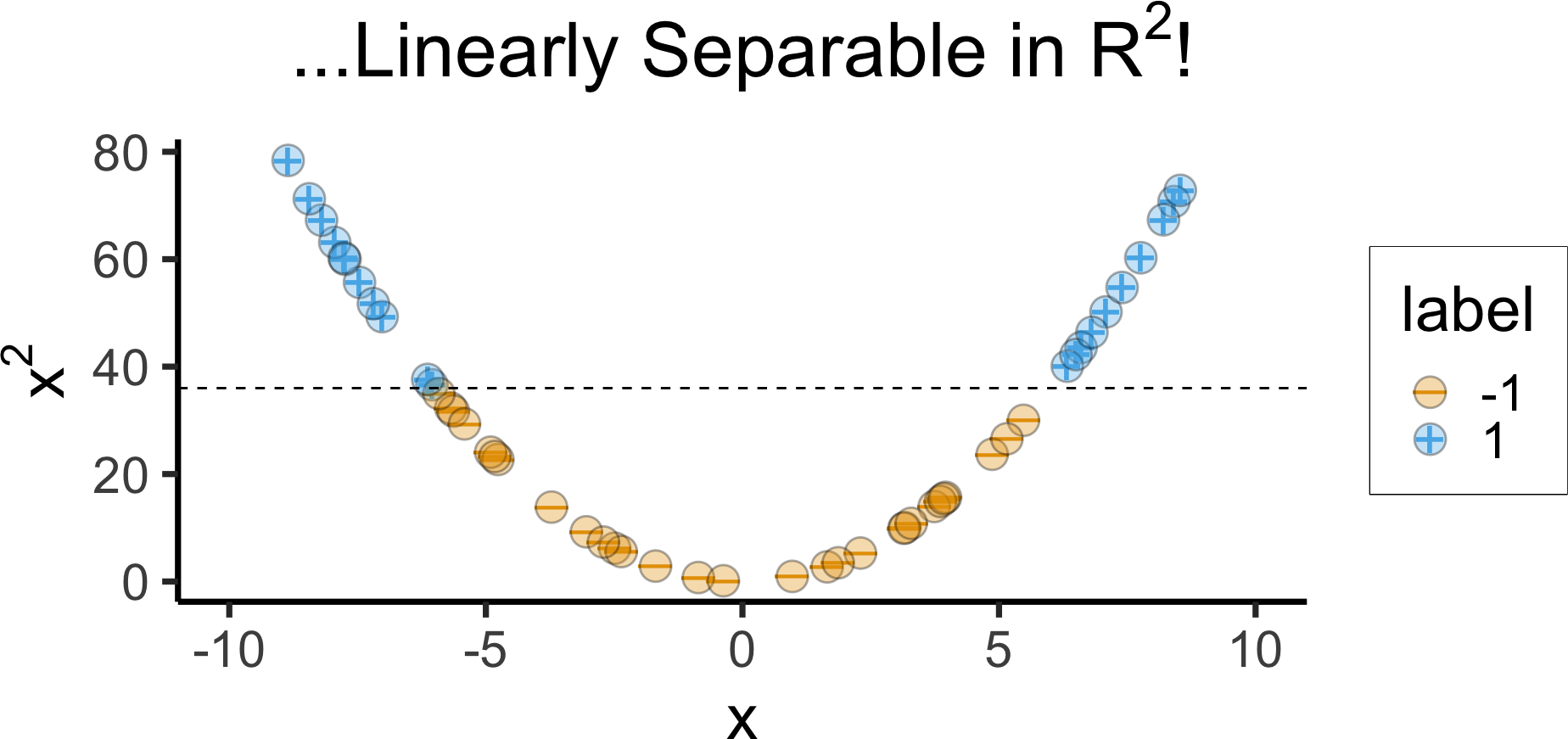
- Helpful example: Non-linearly separable in 1D \(\leadsto\) Linearly separable in 2D
1D Hyperplane = point! But no separating point here 😰
Code
library(latex2exp) |> suppressPackageStartupMessages()
x_vals <- runif(50, min=-9, max=9)
data_df <- tibble(x=x_vals) |> mutate(
label = factor(ifelse(abs(x) >= 6, 1, -1)),
x2 = x^2
)
data_df |> ggplot(aes(x=x, y=0, color=label)) +
geom_point(
aes(color=label, shape=label), size=g_pointsize,
stroke=6
) +
geom_point(
aes(fill=label), color='black', shape=21, size=6, stroke=0.75, alpha=0.333
) +
# xlim(6,25) + ylim(2,22) +
# coord_equal() +
# 45 is minus sign, 95 is em-dash
scale_shape_manual(values=c(95, 43)) +
theme_dsan(base_size=28) +
theme(
axis.line.y = element_blank(),
axis.text.y = element_blank(),
axis.ticks.y = element_blank(),
axis.title.y = element_blank()
) +
xlim(-10, 10) +
ylim(-0.1, 0.1) +
labs(title="Non-Linearly-Separable Data") +
theme(
plot.margin = unit(c(0,0,0,20), "mm")
)
Code
data_df |> ggplot(aes(x=x, y=x2, color=label)) +
geom_point(
aes(color=label, shape=label), size=g_pointsize,
stroke=6
) +
geom_point(
aes(fill=label), color='black', shape=21, size=6, stroke=0.75, alpha=0.333
) +
geom_hline(yintercept=36, linetype="dashed") +
# xlim(6,25) + ylim(2,22) +
# coord_equal() +
# 45 is minus sign, 95 is em-dash
scale_shape_manual(values=c(95, 43)) +
theme_dsan(base_size=28) +
xlim(-10, 10) +
labs(
title = TeX("...Linearly Separable in $R^2$!"),
y = TeX("$x^2$")
)
And in 3D…
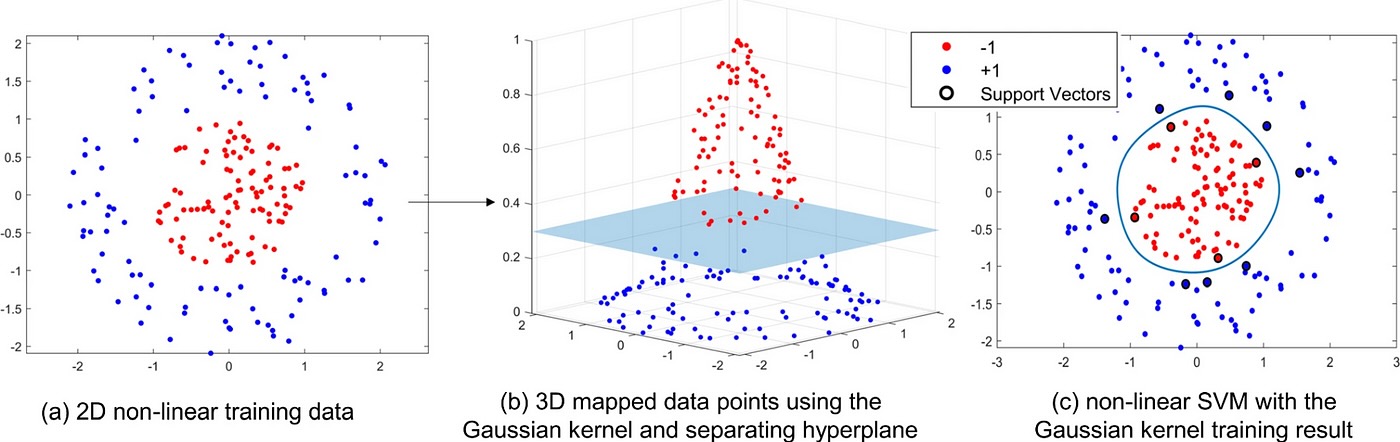
Taking This Idea and Running With It
- The goal: find a transformation of the original space that the (non-linearly-separable) data lives in, such that data is linearly separable in new space
- In theory, could just compute tons and tons of new features \(\{X_1, X_1^2, X_1^3, \ldots, X_1X_2, X_1X_3, \ldots, X_1^2X_2, X_1^2X_3, \ldots\}\)
- In practice this “blows up” the dimensionality of the feature space, making SVM slower and slower
- Weird trick (literally): turns out we only need inner products \(\langle x_i, x_j \rangle\) between datapoints… “Kernel Trick”
The Magic of Kernels
Radial Basis Function (RBF) Kernel:
\[ K(x_i, x_{i'}) = \exp\left[ -\gamma \sum_{j=1}^{J} (x_{ij} - x_{i'j})^2 \right] \]
Code
library(kernlab) |> suppressPackageStartupMessages()
library(mlbench) |> suppressPackageStartupMessages()
if (!file.exists("assets/linspike_df.rds")) {
set.seed(5300)
N <- 120
x1_vals <- runif(N, min=-5, max=5)
x2_raw <- x1_vals
x2_noise <- rnorm(N, mean=0, sd=1.25)
x2_vals <- x2_raw + x2_noise
linspike_df <- tibble(x1=x1_vals, x2=x2_vals) |>
mutate(
label = factor(ifelse(x1^2 + x2^2 <= 2.75, 1, -1))
)
linspike_svm <- ksvm(
label ~ x1 + x2,
data = linspike_df,
kernel = "rbfdot",
C = 500,
prob.model = TRUE
)
# Grid over which to evaluate decision boundaries
npts <- 500
lsgrid <- expand.grid(
x1 = seq(from = -5, 5, length = npts),
x2 = seq(from = -5, 5, length = npts)
)
# Predicted probabilities (as a two-column matrix)
prob_svm <- predict(
linspike_svm,
newdata = lsgrid,
type = "probabilities"
)
# Add predicted class probabilities
lsgrid2 <- lsgrid |>
cbind("SVM" = prob_svm[, 1L]) |>
tidyr::gather(Model, Prob, -x1, -x2)
# Serialize for quicker rendering
saveRDS(linspike_df, "assets/linspike_df.rds")
saveRDS(lsgrid2, "assets/lsgrid2.rds")
} else {
linspike_df <- readRDS("assets/linspike_df.rds")
lsgrid2 <- readRDS("assets/lsgrid2.rds")
}
linspike_df <- linspike_df |> mutate(
Label = label
)
linspike_df |> ggplot(aes(x = x1, y = x2)) +
# geom_point(aes(shape = label, color = label), size = 3, alpha = 0.75) +
geom_point(aes(shape = Label, color = Label), size = 3, stroke=4) +
geom_point(aes(fill=Label), color='black', shape=21, size=4, stroke=0.75, alpha=0.4) +
xlab(expression(X[1])) +
ylab(expression(X[2])) +
coord_fixed() +
theme(legend.position = "none") +
theme_dsan(base_size=28) +
xlim(-5, 5) + ylim(-5, 5) +
stat_contour(
data = lsgrid2,
aes(x = x1, y = x2, z = Prob),
breaks = 0.5,
color = "black"
) +
scale_shape_manual(values=c(95, 43))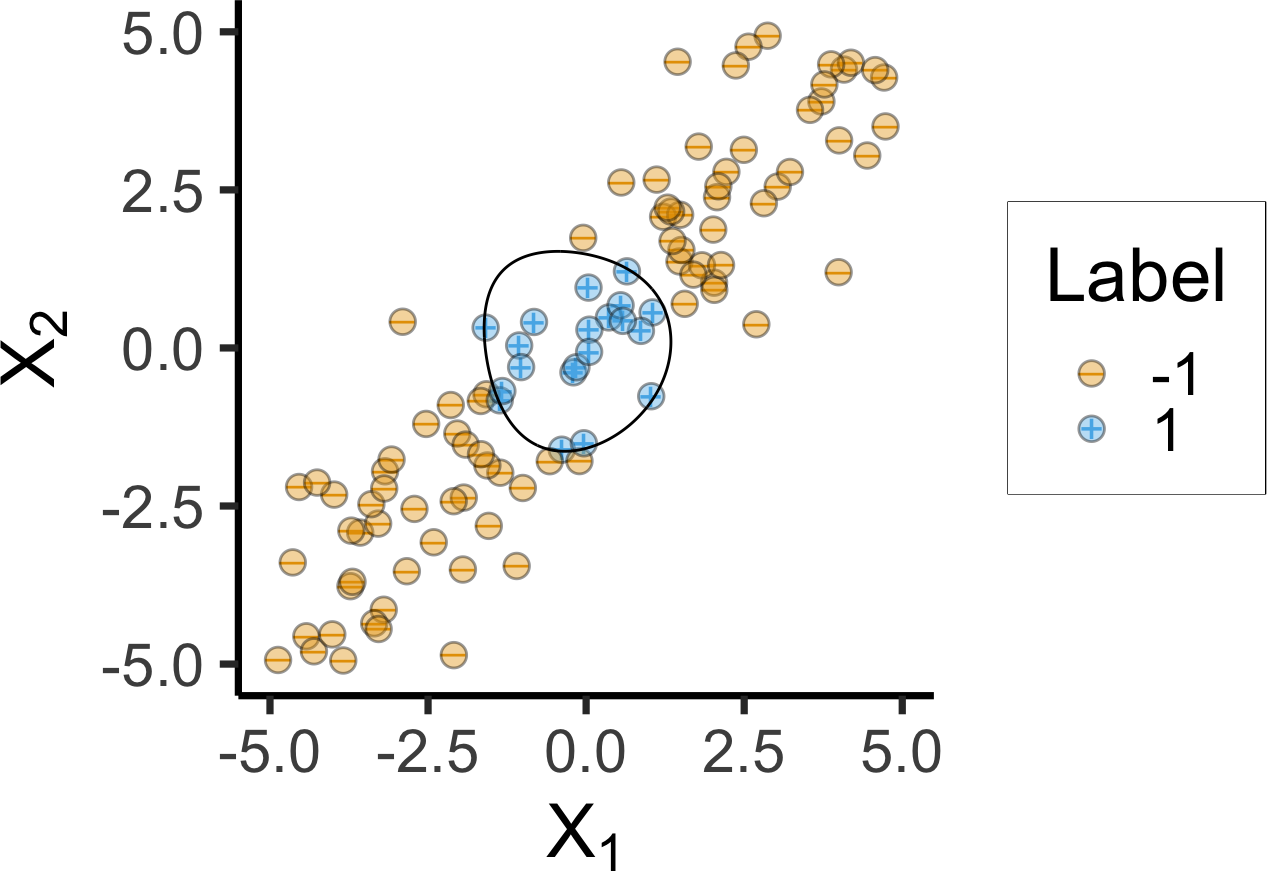
Code
if (!file.exists("assets/spiral_df.rds")) {
spiral_df <- as.data.frame(
mlbench.spirals(300, cycles = 2, sd = 0.09)
)
names(spiral_df) <- c("x1", "x2", "label")
# Fit SVM using a RBF kernel
spirals_svm <- ksvm(
label ~ x1 + x2,
data = spiral_df,
kernel = "rbfdot",
C = 500,
prob.model = TRUE
)
# Grid over which to evaluate decision boundaries
npts <- 500
xgrid <- expand.grid(
x1 = seq(from = -2, 2, length = npts),
x2 = seq(from = -2, 2, length = npts)
)
# Predicted probabilities (as a two-column matrix)
prob_svm <- predict(
spirals_svm,
newdata = xgrid,
type = "probabilities"
)
# Add predicted class probabilities
xgrid2 <- xgrid |>
cbind("SVM" = prob_svm[, 1L]) |>
tidyr::gather(Model, Prob, -x1, -x2)
# Serialize for quicker rendering
saveRDS(spiral_df, "assets/spiral_df.rds")
saveRDS(xgrid2, "assets/xgrid2.rds")
} else {
spiral_df <- readRDS("assets/spiral_df.rds")
xgrid2 <- readRDS("assets/xgrid2.rds")
}
# And plot
spiral_df <- spiral_df |> mutate(
Label = factor(ifelse(label == 2, 1, -1))
)
spiral_df |> ggplot(aes(x = x1, y = x2)) +
geom_point(aes(shape = Label, color = Label), size = 3, stroke=4) +
geom_point(aes(fill=Label), color='black', shape=21, size=4, stroke=0.75, alpha=0.4) +
xlab(expression(X[1])) +
ylab(expression(X[2])) +
xlim(-2, 2) +
ylim(-2, 2) +
coord_fixed() +
theme(legend.position = "none") +
theme_dsan(base_size=28) +
stat_contour(
data = xgrid2,
aes(x = x1, y = x2, z = Prob),
breaks = 0.5,
color = "black"
) +
scale_shape_manual("Label", values=c(95, 43))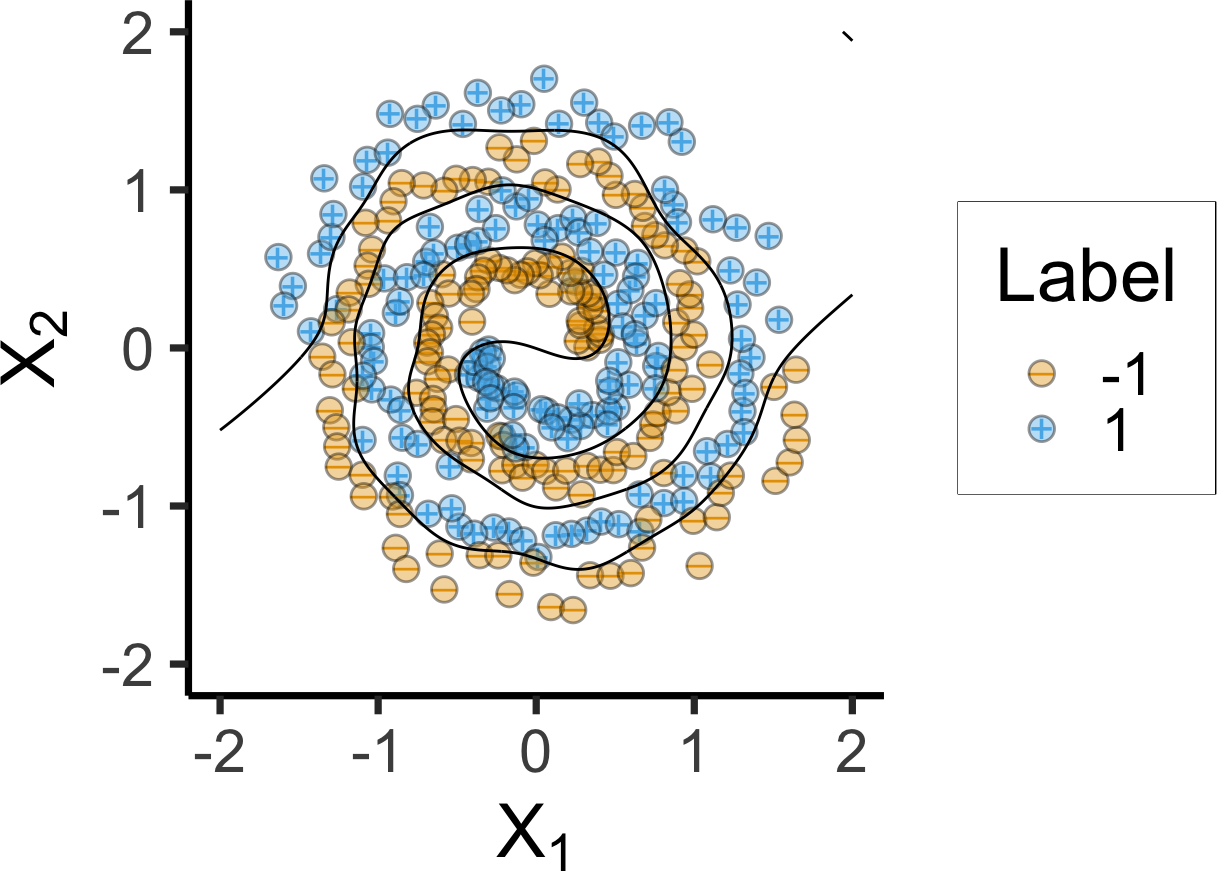
How Is This Possible?
- SVM prediction for an observation \(\mathbf{x}\) can be rewritten as
\[ f(\mathbf{x}) = \beta_0 + \sum_{i=1}^{n} \alpha_i \langle \mathbf{x}, \mathbf{x}_i \rangle \]
- Rather than one parameter \(\beta_j\) per feature, we have one parameter \(\alpha_i\) per observation
- At first this seems worse, since usually \(n > p\)… But we’re saved by support vectors!
- Since the margin itself is only a function of the support vectors (not every vector—remember that margin \(\neq\) average distance!), \(\alpha_i > 0\) only when \(\mathbf{x}_i\) a support vector!
- Thus the equation becomes \(f(\mathbf{x}) = \beta_0 + \sum_{i \in \mathcal{SV}} \alpha_i \langle \mathbf{x}, \mathbf{x}_i \rangle\), and there’s one step left…
- Kernel \(K\) = similarity function (generalization of inner product!)
\[ f(\mathbf{x}) = \beta_0 + \sum_{i \in \mathcal{SV}} \alpha_i K(\mathbf{x}, \mathbf{x}_i) \]
Inner Products are Already Similarities!
- When linearly separable, this is exactly the property we use (by computing inner product of new vector \(\mathbf{x}\) with support vectors \(\mathbf{x}_i\)) to classify!
- Why restrict ourselves to this similarity function? Choosing \(K\) converts the problem:
- From finding transformation of features allowing linear separability
- To finding similarity function for observations allowing linear separability
Kernel Trick as Two-Sided Swiss Army Knife
If we have a linearly-separating transformation (like \(f(x) = x^2\)), can “encode” as kernel, saving computation
Example: Transformation of features \(f(x) = x^2\) equivalent to quadratic kernel:
\[ K(x_i, x_{i'}) = (1 + \sum_{j = 1}^{p}x_{ij}x_{i'j})^2 \]
If we don’t have a transformation (and having trouble figuring it out), can change the problem into one of finding a “good” similarity function
Example: Look again at RBF Kernel:
\[ K(x_i, x_{i'}) = \exp\left[ -\gamma \sum_{j=1}^{J} (x_{ij} - x_{i'j})^2 \right] \]
It turns out: no finite collection of transformed features is equivalent to this kernel! (Roughly: can keep adding transformed features to asymptotically approach it—space of SVMs w/kernel thus \(>\) space of SVMs w/transformed features)
References
DSAN 5300-01 Week 8: Support Vector Machines (SVMs)