| name | pop | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Albania | 2.8 |
| 1 | Algeria | 44.2 |
| 2 | Angola | 34.5 |
Week 2: Nuts and Bolts for Data Science
DSAN 5000: Data Science and Analytics
Thursday, September 5, 2024
Computer fundamentals
A little basic computer science is very useful for all STEM fields!
Motivation
Understanding how computers work is crucial for data scientists
- Efficient Coding: Proficiency in computer architecture helps optimize code for faster processing & memory management.
- Algorithm Design: A grasp of hardware aids in designing algorithms tailored to the computer’s capabilities.
- Data Handling: Efficient data storage, retrieval, & manipulation improve performance with large datasets.
- Resource usage: Knowledge of system resources enables optimal utilization & scalability of compute power.
- Problem Solving: Understanding hardware enables better debugging & identifying performance bottlenecks.
- Collaboration: Effective communication with IT teams & hardware experts enhances cross-functional projects.
- Career Versatility: Understanding opens doors to diverse roles, from machine learning to system optimization.
- Continuous Learning: As technology evolves, foundational computer knowledge helps adapt to new tools
Note: These skills become very important in DSAN-6000 (big data & cloud computing)
Hardware
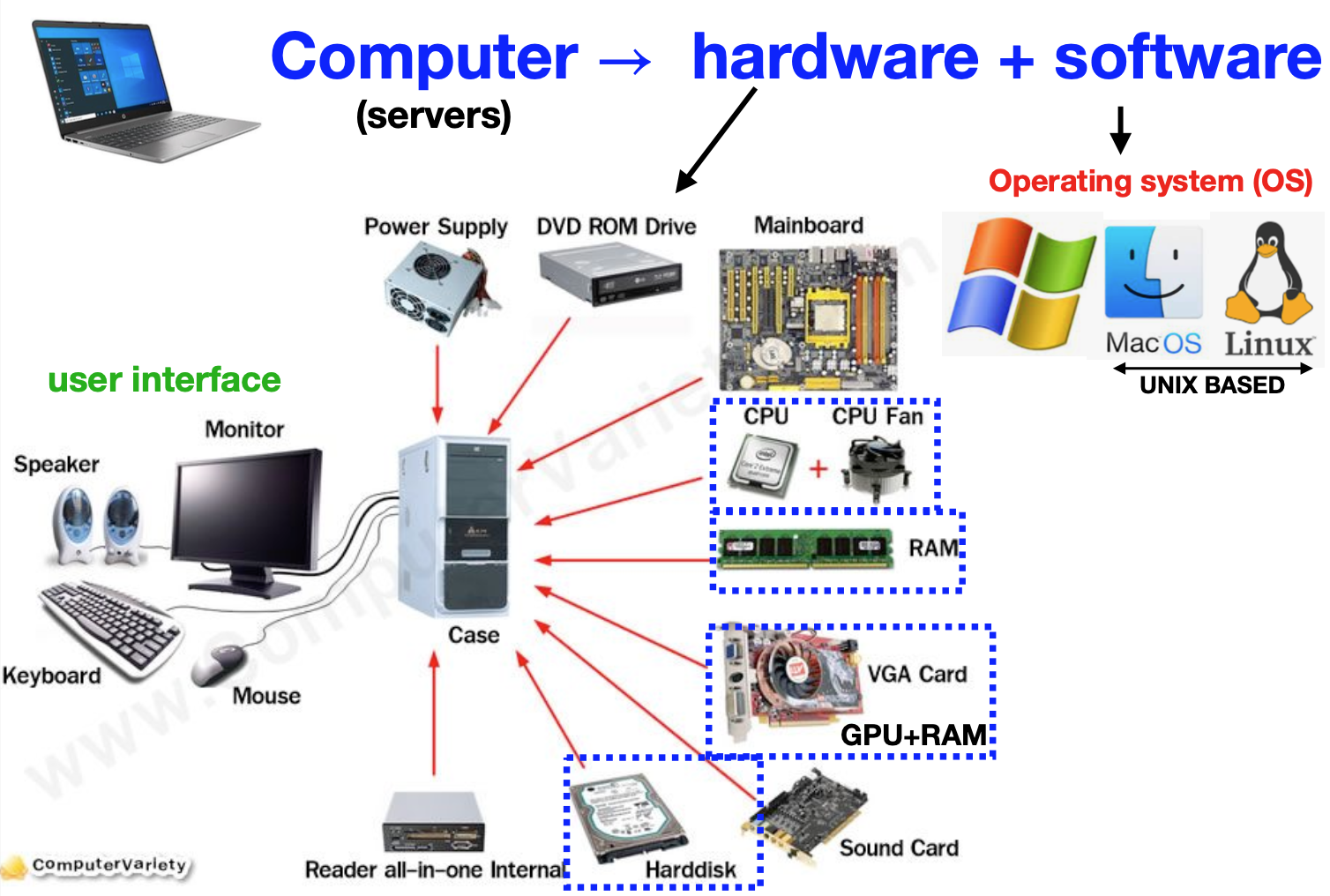
Physical components of a computer
Computer form factors
Computers come in many shapes & sizes, however, they’re all basically the same inside
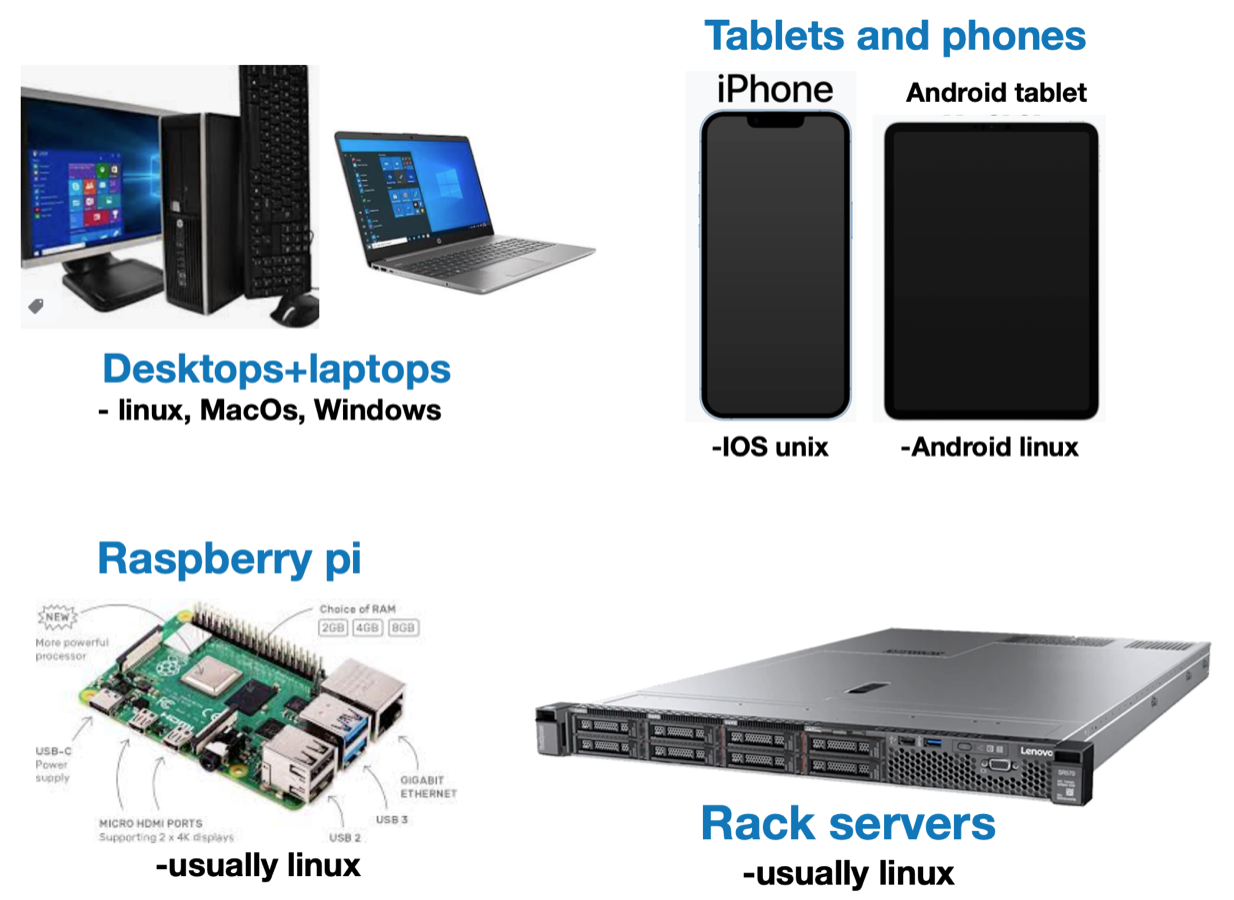
Hardware components
- Broadly speaking, the following are the fundamental components of all computers:
![]()
Computer hardware
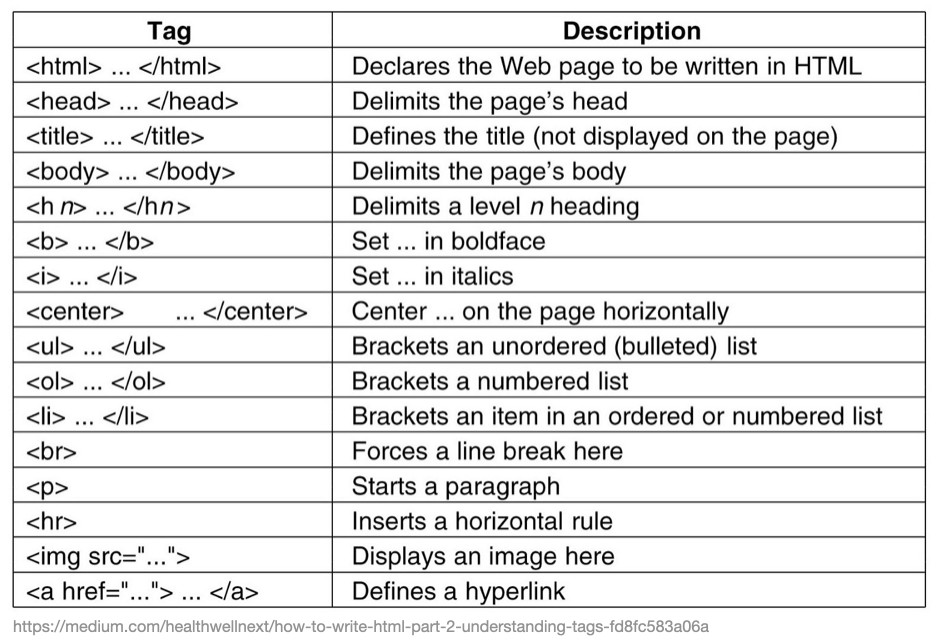
Read over the following at home- In general, computers consist of several fundamental components, including
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Executes instructions, performs calculations, & manages tasks, acting as the computer’s brain.
- Motherboard: Main circuit board connecting all components, providing communication & power distribution pathways.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): Offers fast-access memory for active programs, enhancing multitasking & performance.
- Storage Drives: Include Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) for high-capacity storage and Solid State Drives (SSDs) for faster data access.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): Converts and supplies power to components, ensuring stable operation.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): Handles graphical computations, vital for video rendering, gaming, and complex visuals.
- Cooling System: Comprises fans, heat sinks, and sometimes liquid cooling to dissipate heat and prevent overheating.
- Case/Chassis: Houses and protects components, facilitating airflow and accommodating expansion.
- Input/Output Ports: Enable connection to external devices, such as USB, audio, video, and networking ports.
- Optical Drive: Reads and writes optical discs like CDs, DVDs, or Blu-rays (optional in modern systems).
- Expansion Slots: Allow adding extra components like graphics cards, sound cards, or network adapters.
- Operating System: Software interface managing hardware resources, enabling software execution and user interaction.
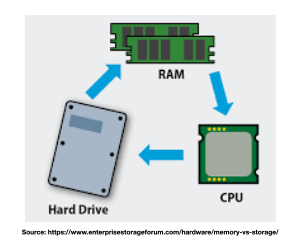
Storage vs memory
- Memory (RAM)
- Short term data storage
- FAST communication with CPU
- Data vanishes when the computer is shut-off (short term memory)
- Storage (hard-disk)
- Long term data storage
- SLOWER communication with CPU
- Data exists even when the computer is shut-off (permanent storage)
File Systems
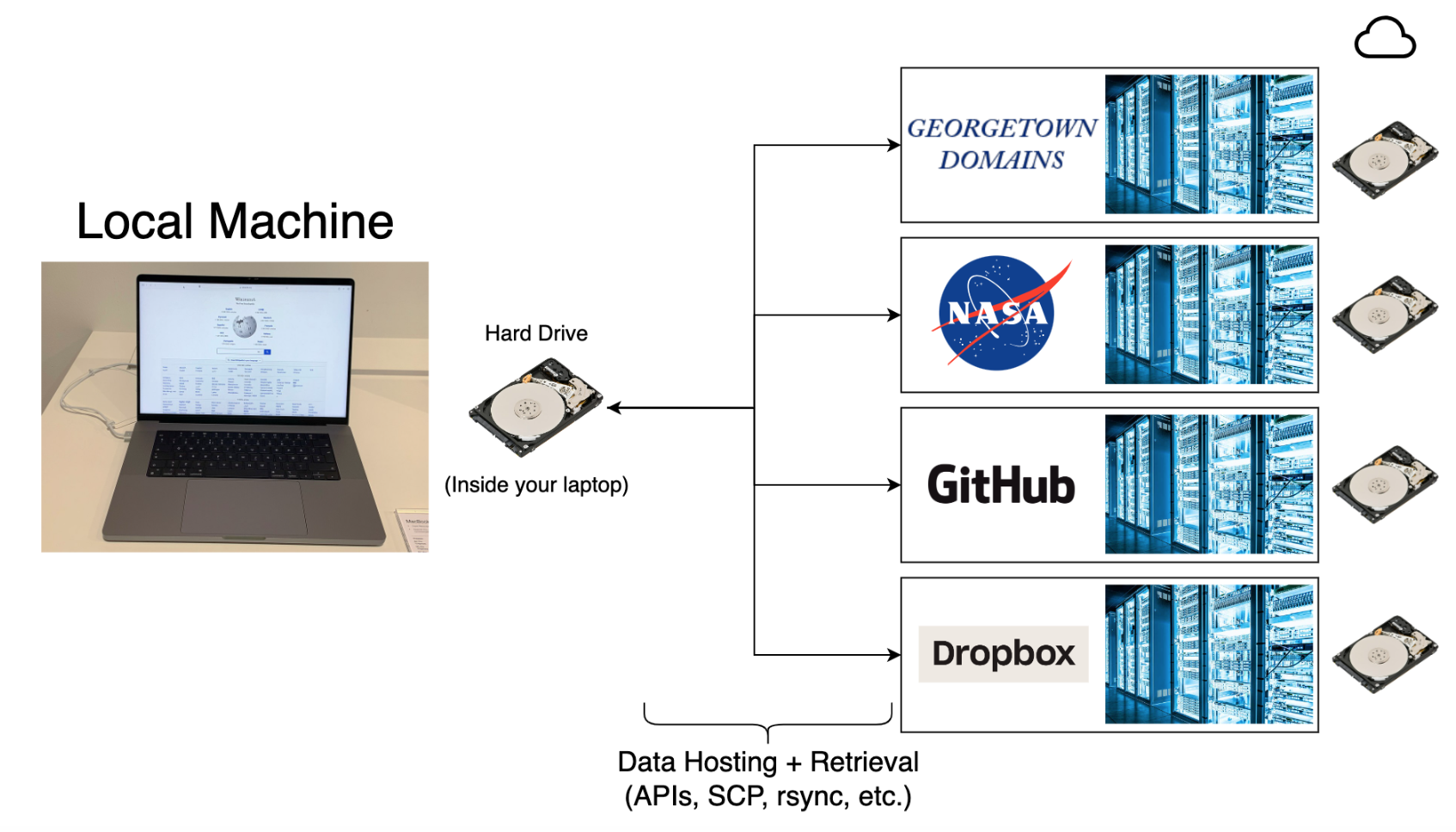
Where does data live?
- All data lives in a
file-systemon ahard-disksomewhere, you CAN’T do data science without understanding file-systems! - A computer file system is a structured method for storing, organizing, & managing files.
![]()
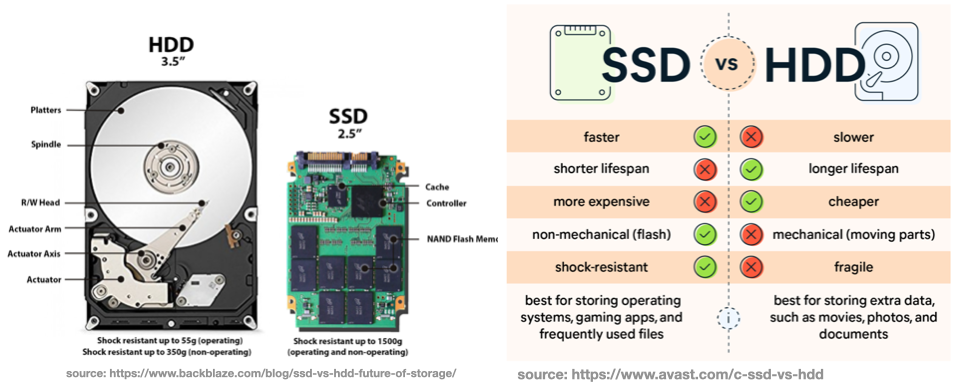
Storage Types
- HDD (older) and SSD (newer) are the current options for computer hard-disks.
![]()
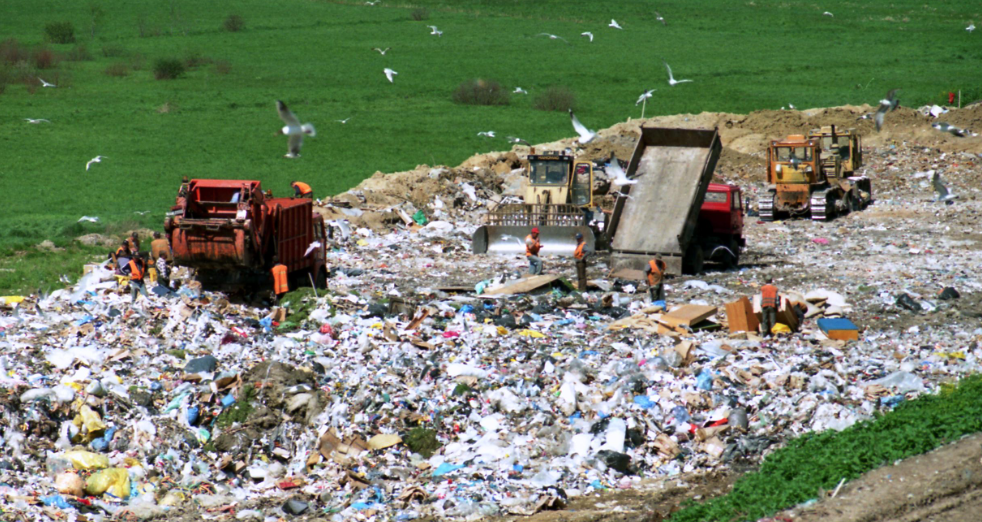
Aside: Modern buried treasure
- In 2012, James Howells threw away a hard drive during an office clear out
- BitCoin was less valuable in 2012, and he forgot there were Bitcoins stored on the disk.
- In 2022, the Bitcoin on the disk was worth an estimated 184 million dollars.
- Howells plans to spend millions digging up a Newport landfill to find the lost hard drive.
![]()
Overview
- Paths & file-system familiarity is essential for accessing & moving data from servers
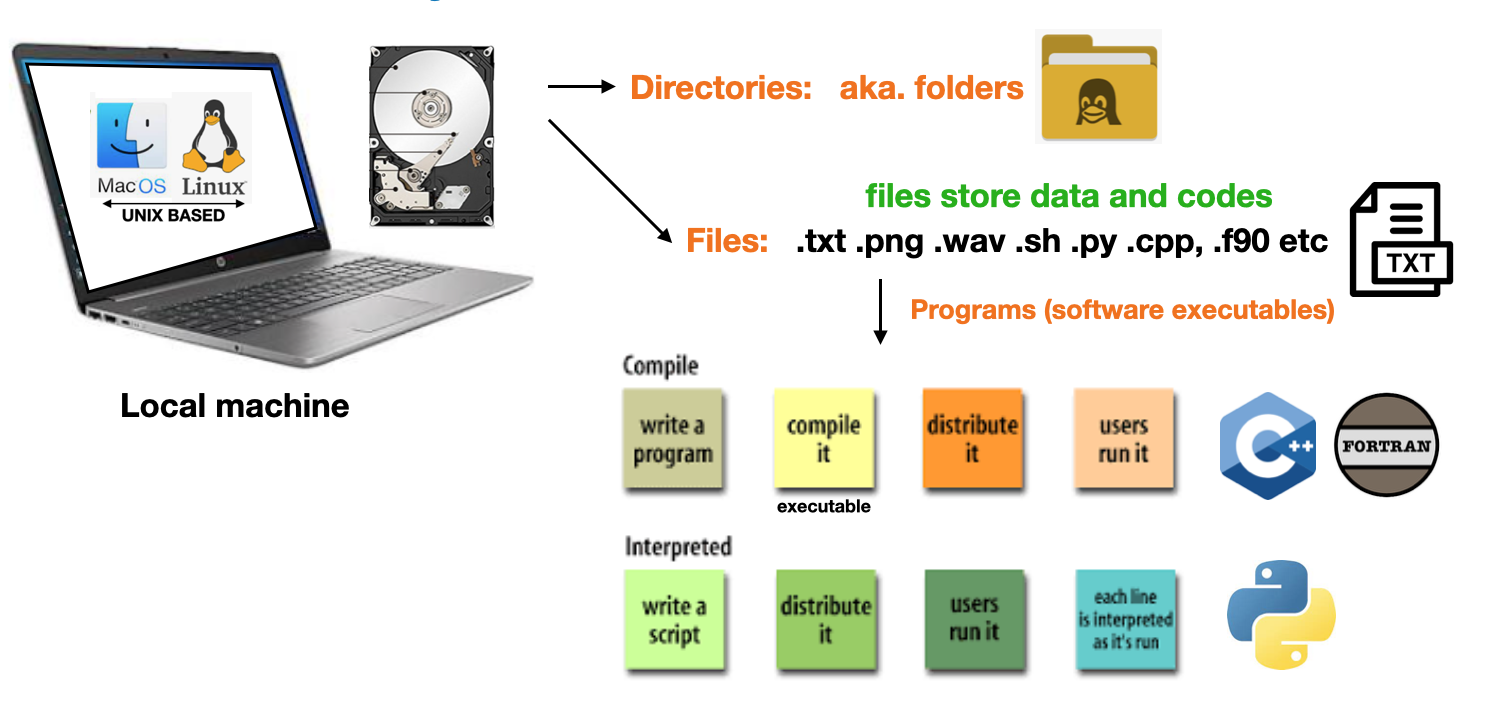
- The file system is composed of
directories(folders),programs, andfiles- The
filescontain data OR instructions forprogramcreation - Files, programs, & folders have associated
permissionsto control user access![]()
- The
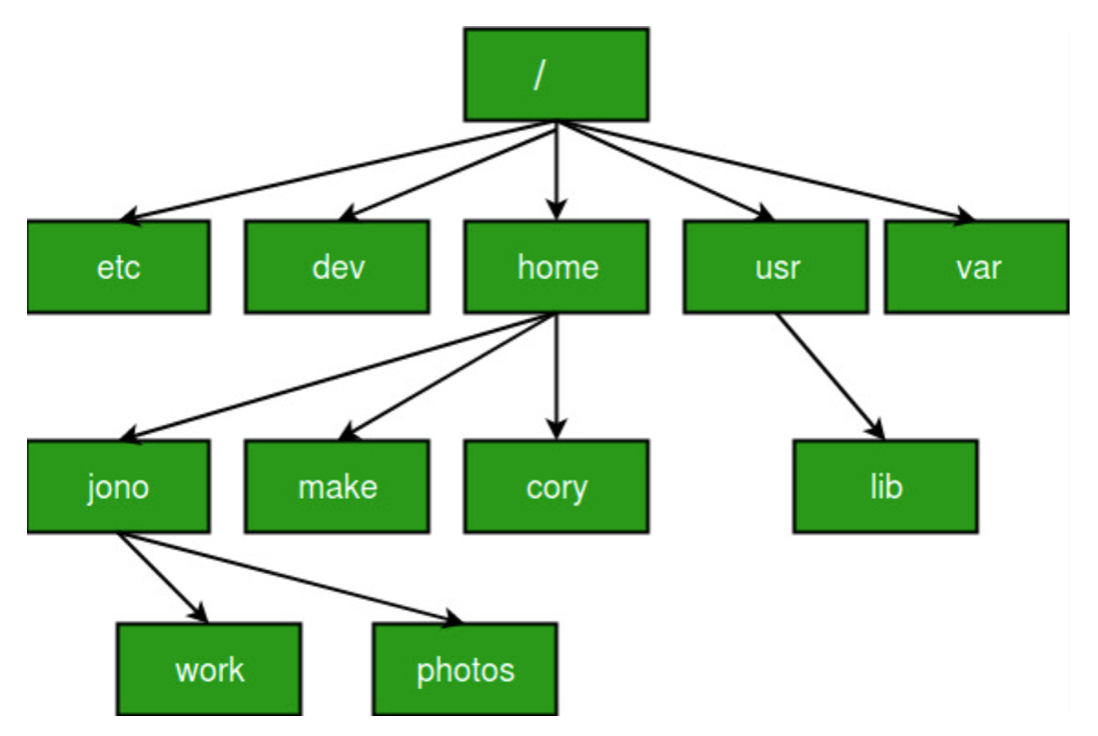
Directory tree
- The Files, folders, & executables are organized in a hierarchical
directory tree - The
baseof the tree is called theroot directory - The root folder is denoted by
/on Unix machines and\on Windows machines![]()
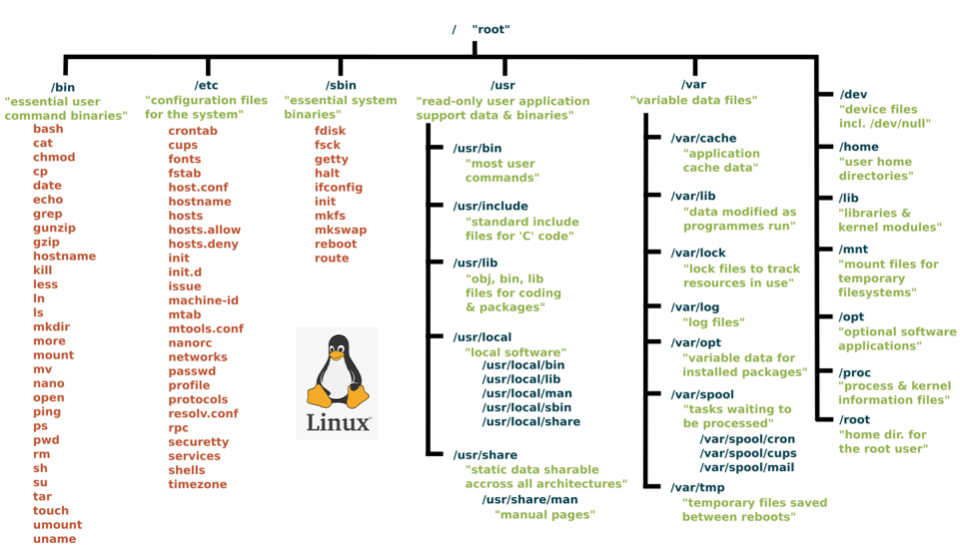
Linux directory tree
- The following diagram shows the directory tree of a Linux computer
![]()
Paths
Pathsare “addresses”, they let users navigate the file-system to locate files & folders- Paths can be either
relative, i.e. a location relative to the currentfolder, ORabsolutelocation relative to therootdirectory - The
current working directory(CWD) is where you currently “are” in the tree. - On Unix, the CWD is denoted
./& one leveldownis denoted../(closer to the root) - The slashes are reversed on windows
\, but otherwise the concept is the same![]()
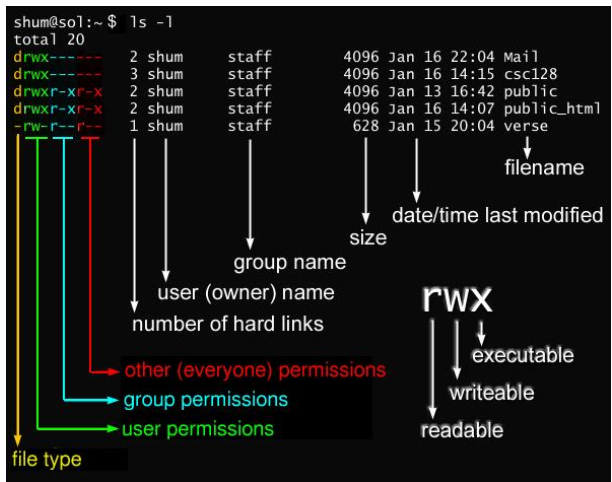
File permissions
System administratorscontrol how muchaccessdifferentusershave with-in the file-structure.- Access is based on file permissions associated with a user’s Login ID
- Computers keep a database of which user owns each files, & which users have permission to view, edit, & execute EACH file, folder, or program.
- Understanding basic data security is a fundamental skill in most modern careers … you don’t want to be the careless person that leaves a software vulnerability and gets your company hacked

Unix file permissions
- Unix file permission codes are numeric representations (octal) for read, write, execute permissions, assigned to owners, groups, and others, regulating file access and security.
![]()
- If a user has authority, they can change file permissions with the
chmodcommand
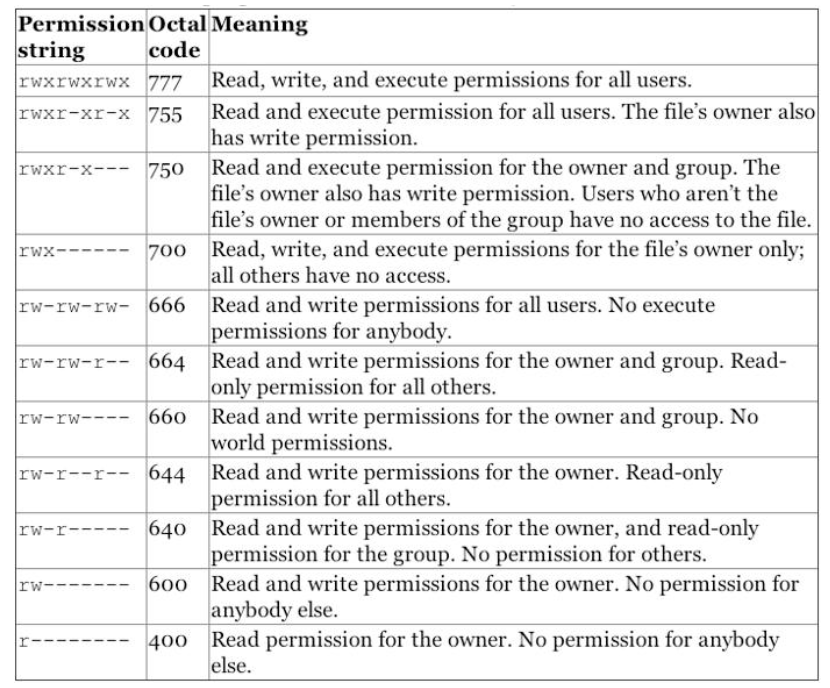
Common file permissions codes
- The following are common permission options.
![]()
NOTE:For websites: files are ususually644and folders755- This could be set with
chmod 644 my_file.html - You can set all website files permssiosn with the following linux commands
for i in $(find _site -type f); do chmod 644 $i; donefor i in $(find _site -type d); do chmod 755 $i; done`
- This could be set with
Super-users
- Super-users have total control over the file-system, can view, edit, or execute anything.
- A SuperUser is synonymous with
root-user, means there is no restrictions on your power over the computer
- A SuperUser is synonymous with
- Usually you are NOT a super-user and you need to coordinate with
system administrators, who have super-user status, to set up and control access

“With great power comes great responsibility”
- The Spider-Man’s Uncle
Linux command line
A brief introduction.

What is Linux?
- Linux describes a family of operating systems (OS), similar to
WindowsorMacOS - The key difference is that
Linuxis aFREEandopen-sourceoperating system.![]()
- It has a
Unix-likeOS kernel originally created byLinus Torvaldsin1991. - It forms the core of various Linux-based operating systems (distributions) such as Ubuntu, CentOS, RedHat, Fedora, and more.
- Linux is known for its stability, security, and flexibility.
- Almost all of the worlds super-computers are Linux machines
- Web-servers & AWS virtual machines are also often Linux (e.g.
GU domains)
Linux key features (optional)
- Linux offers a flexible and powerful platform for various computing needs, from personal use to enterprise-level systems.
- Open Source: Linux’s source code is freely available, allowing users to modify, distribute, and contribute to its development.
- Kernel: Linux serves as the core of the operating system, managing hardware resources, memory, and system processes.
- Multiuser and Multitasking: Linux supports multiple users and concurrent tasks, enhancing efficiency.
- Security: Linux’s design and permissions system offer robust security features, minimizing vulnerabilities.
- Variety of Distributions: Different Linux distributions cater to diverse needs, from server systems to desktop environments.
- Command Line Interface: Linux offers a powerful command line interface (CLI) for system management and administration.
- Graphical User Interface: Most Linux distributions include GUI options, making it user-friendly for various users.
- Software Repositories: Distributions provide software repositories for easy installation and updates of applications.
- Networking: Linux is widely used for networking, powering servers, routers, and other network devices.
- Customization: Users can customize various aspects of their Linux environment, adapting it to their preferences.
- Server and Cloud Usage: Linux is a popular choice for web servers, cloud computing, & containerization platforms like Docker.
- Community and Support: The Linux community provides extensive support, forums, and documentation resources.
Why learn the Linux command line?
Useful line on your resume- Intuitive framework and tool-set for computational sciences
- Better understanding of system and network administration
- Almost all of the worlds super-computers are Linux machines
- Web-servers and AWS virtual machines are often Linux
- More intuitive interfacing with hardware and software
- Smoothly interact with GitHub without using a web browser or GUI
- Smoothly switch between environments with Conda
- Can “get inside” other computers via the
ssh command
Example: Can “get inside” other computers via the ssh command

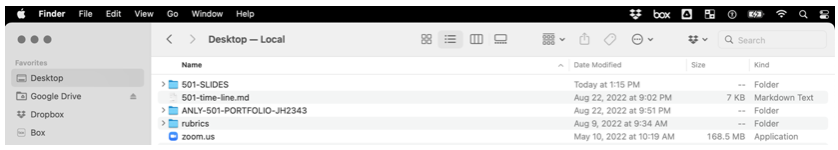
Interacting with the file-system
Option-1:Interact with the file system via a GUI (graphical user interface)![]()
Option-2:Interact via a command line interface(CLI)![]()
-
IMPORTANT:The Unix command line is actually more like a computer scripting language (e.g. python), known asshell scriptingorbash. It has all of the familiar coding constructs (for-loops, while loops, if/then statements, … etc) -
Hidden files: Files & folders that start with.are hidden from the GUI interface (e.g.~.bash_profile)
Command line access options
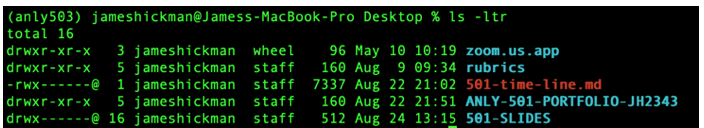
Mac & Linux:MacOS is very similar to Linux, both have a built-inUnixCLI.
![]()
Windowsterminal options:- Command prompt: A text-based interface to execute commands and perform tasks
- NOT a Unix CLI, closer to
MS-DOS, completely different command structure
- NOT a Unix CLI, closer to
- Windows powershell: Windows PowerShell is an advanced command-line shell and scripting language for automation and system management.
- NOT a Unix command line, but more “Unix-like” than command prompt
- Anaconda powershell: Quasi Unix command structure but still quite different
- Windows subsystem for Linux (WSL): (
highly recommended)- True Linux experience from within Windows,
more on this later
- True Linux experience from within Windows,
- Command prompt: A text-based interface to execute commands and perform tasks
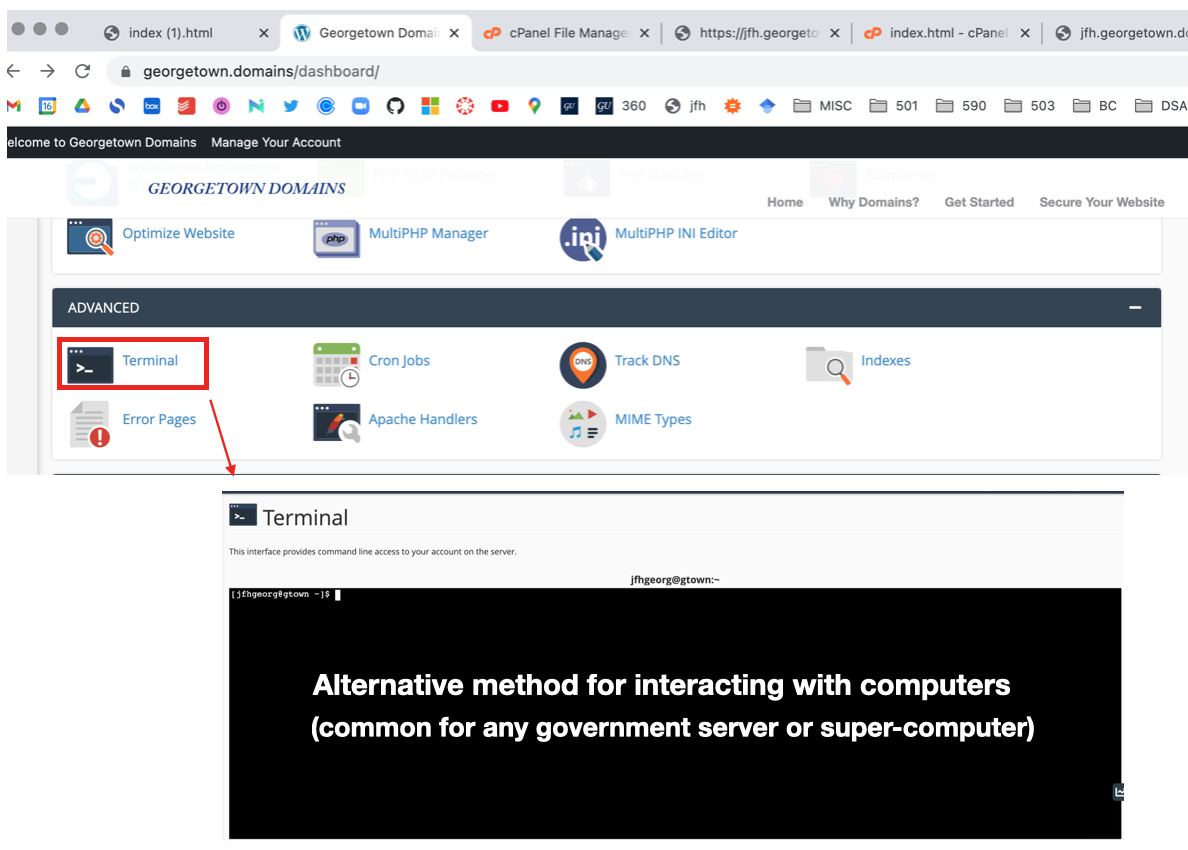
GU domains: Command line access
- The
GU domainsweb-servers are Linux, you can “get inside” the servers via a browser- You can also
sshinside from your laptop (more on this next week)![]()
- You can also
- Note: that you are NOT inside your laptop here!! But rather the GU-domains server, which is just a REMOTE computer located somewhere else in the world (e.g. California or China).
Linux commands & variables
- Everything we discuss on the coming slides applies to (1) Linux CLI, (2) WSL in Windows, (3) the MacOS CLI (although minor differences do exist)
Linux Commands- A Linux command generally follows the following structure:
command [options/flags] [arguments]- Command: The primary action or task that you want the command to perform.
- Options/Flags: These are preceded by a hyphen
-or double hyphen--and modify the behavior of the command. They are usually optional. - Arguments: Targets or inputs for the command (files, directories, text, etc).
Linux Variables- Variables are typically denoted using uppercase letters & underscores, e.g. MY_VARIABLE. Values are assigned with
variable_name=value - Use
$before the variable name to access its value, e.g$MY_VARIABLE.
- Variables are typically denoted using uppercase letters & underscores, e.g. MY_VARIABLE. Values are assigned with
Command example: ls
For example, let’s take the ls command and describe its structure with flags:
ls [options/flags] [arguments]
- Command:
lsstands for “list” and is used to list files and directories. - Options/Flags:
-lor--long: Display detailed information about files.-aor--all: List all files, including hidden ones.-hor--human-readable: Display file sizes in a human-readable format.
- Arguments: These would be the directories or files you want to list.
- For instance,
ls -l /path/to/directory.
- For instance,
- You can use multiple options and arguments with a command to customize its behavior. Always refer to the command’s manual or help documentation (usually accessible with
man commandorcommand --help) to understand all available options and how they affect the command’s behavior.
(1) Navigating the file system
pwd: Print the current working directory (current location in the directory tree)pwd ../: Print the path of the directory one level above the current directory.ls: List files and directories in the current directory.ls ../: List files and directories in the directory one level above.ls ./: List files and directories in the current directory.- IMPORTANT: The symbol
*acts as awild-cardto search for substrings ls *pub*: List files and directories with names containing “pub”.ls -d *pub*: List directories only with names containing “pub”.ls *pub*/*.html: List.htmlfiles inside directories with names containing “pub”.- IMPORTANT: You can run multiple commands per line using
;to separate them ls *pub*; ls *pub*/*.html:- Run two
lscommands on one line with;separating them.
- Run two
(2) Navigating the file system
- cd: Change directory (folder). Navigate to a different folder in the file system.
cd public_html/: Change current directory topublic_html/.cd ../: Move to the directory one level closer to theroot.- Note:
../is “down” if you think of the “root” as the bottom of the computer & “up”, if you think of therootas the top of the computer. Both are terminology are common, just know that../takes you closer to therootdirectory
- Note:
cd files: Change current directory to “files”.cd public_html/: Change current directory topublic_html/.cd ~/: Change to the home directory (usually/home/username).cd public_html/: Change current directory topublic_html/.find -name index.html: Search for a file namedindex.html.find -name index*: Search for files starting with “index”.
Viewing file content
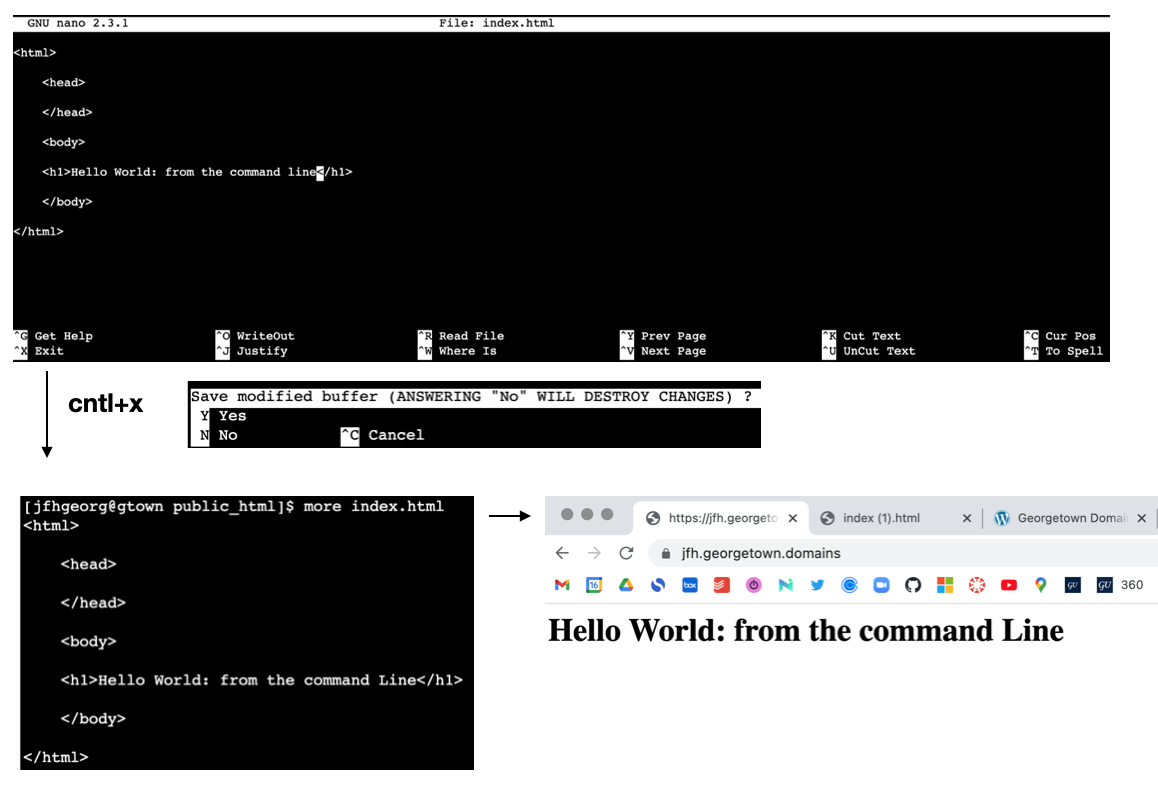
more index.html: View the contents ofindex.htmlusing themorecommand.more page2.html: View the contents of “page2.html”.less index.html: View the contents using thelesscommand (pressqto exit).head index.html: Display the beginning lines ofindex.html.tail index.html: Display the last lines ofindex.html.tail -n 4 index.html: Display the last 4 lines ofindex.html.grep 'Hello' index.html: Search for the string “Hello” inindex.html.- Aside: good practice \(\rightarrow\) avoid using spaces in folder-names and files-names
My Folder\(\rightarrow\)My-FolderORmy_folder- Spaces require an escape symbol
\when writing the pathMy\ Folder
Changing the filesystem
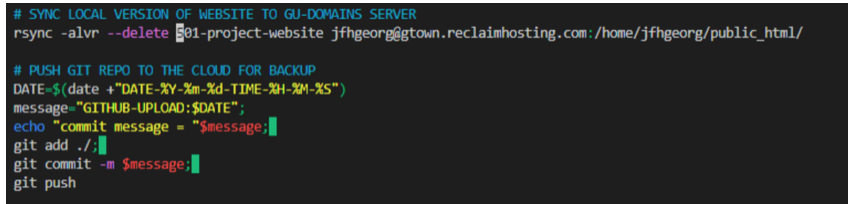
mkdir: Make directory \(\rightarrow\) Creates a new directory. (e.g.mkdir my_folder)rm: Remove files or directories \(\rightarrow\) Deletes files and folders.WARNING:Be CAREFUL withrm, it’sirreversible(deletes file permanently)RECOMMENDATION: (1) ALWAYS work in a folder that is automatically backed up to the cloud (e.g. Dropbox) (2) Push changes to Git-Hub regularly (secondary backup).rm my_file: deletes file calledmy_filerm -rf my_folder: deletes folder calledmy_folder(requires-rflag)
cp: Copy files or directories \(\rightarrow\) Duplicates files and folders.mv: Move or rename files/directories \(\rightarrow\) Used for both moving and renaming.cp ../index.html ./page3.html: Copyindex.htmlone directory closer to root and rename it “page3.html”.cp -r folder_1 folder_2make a copy of a folder (requires recursive-rflag)> page2.html: Create a blank file named “page2.html”.
Shell (bash) scripts
- The command line is a scripted language, similar to Python!!!
- In a
shell script, you can place multiple Linux commands into a file to run sequentially- These are called
shell(.sh) orbashscripts - Similar to python (.py), but with Linux commands, instead of python commands
- You need to change the permissions to make the script executable
chmod a+x my_script.sh - To run the script you use
./my_script.shfrom within the relevant folder
- These are called
Example:Simple example of a shell script![]()
Be careful: This is advanced content, you should only create very simple scripts, unless you know what you are doing.- In particular, we highly recommend NOT USING the
rmcommand in a shell script
- In particular, we highly recommend NOT USING the
Additional important commands (optional)
- These commands are foundational for navigating, managing files, and interacting with a Linux system effectively.
- touch: Create empty files or update timestamps \(\rightarrow\) Creates new empty files or modifies timestamps.
- cat: Concatenate and display file contents \(\rightarrow\) Displays the content of a file in the terminal.
- nano/vi: Text editors \(\rightarrow\) nano
is user-friendly,vi` is powerful but has a steeper learning curve. - echo: Print text to the terminal or a file \(\rightarrow\) Displays text or variables in the terminal.
- grep: Search for text patterns in files \(\rightarrow\) Searches for specific text patterns in files.
- chmod: Change file permissions \(\rightarrow\) Modifies access permissions for files and directories.
- chown: Change file ownership \(\rightarrow\) Changes the owner of files and directories.
- ps: Process status \(\rightarrow\) Lists running processes.
- top/htop: Monitor system resources.
topprovides real-time process monitoring andhtopis a more user-friendly alternative.
- df: Disk space usage \(\rightarrow\) Shows available disk space on filesystems.
- du: Disk usage of files and directories \(\rightarrow\) Displays the space used by specific files or directories.
- wget/curl: Download files from the web \(\rightarrow\)
wgetandcurlcan download files from URLs. - tar: Compress and extract files \(\rightarrow\) Used for archiving and compressing files and directories.
- ssh: Secure Shell \(\rightarrow\) Connects to remote servers securely.
- sudo: Superuser do \(\rightarrow\) Executes commands with
superuser privileges. - history: Show a history of commands entered in the terminal.
Aside: Command line editors (optional)
- You may find yourself inside a server without GUI access \(\rightarrow\) use a command line editor
Nanois a popular command line editor for coding from the command line- e.g.
nano index.html
![]()
- e.g.
- Other popular options include
emacsandvim(not recommended)
Additional reading (optional)
- If you want to learn more, the following are popular books on the topic
![]()
HTML / CSS / JS
Motivation
Due to the internet, media consumption has changed dramatically over the last 30 years.
Traditional media
- Journals, Magazines, academic articles, Billboards
- Inherently Passive consumption of static content

Modern media
- web pages, videos digital paper, electronic billboards
- Inherently Active consumption of content with increased user engagement
- Allows for data updates, modifications, interaction, animation, real-time visualization
- Allows personalized, customizable data-driven visualization

The internet
- The four key ingredients of the Web:
- URLs: Uniform Resource Locators, page addresses to link to pages
- HTML: HyperText Markup Language to write web pages
- Pages are written in HTML (HyperText Markup Language), with CSS for styling options, and Javascript for interactivity
- HTML has an easy way to link to another page with a special anchor tag (
<a>). <a href="http://npr.org/">news</a>creates a link for the anchor text “news,” which will cause the browser to fetch the HTML for the page
- CSS & JavaScript: Formatting and scripting of web content
- HTTP: HyperText transfer Protocol for web clients and servers to communicate
Web communication
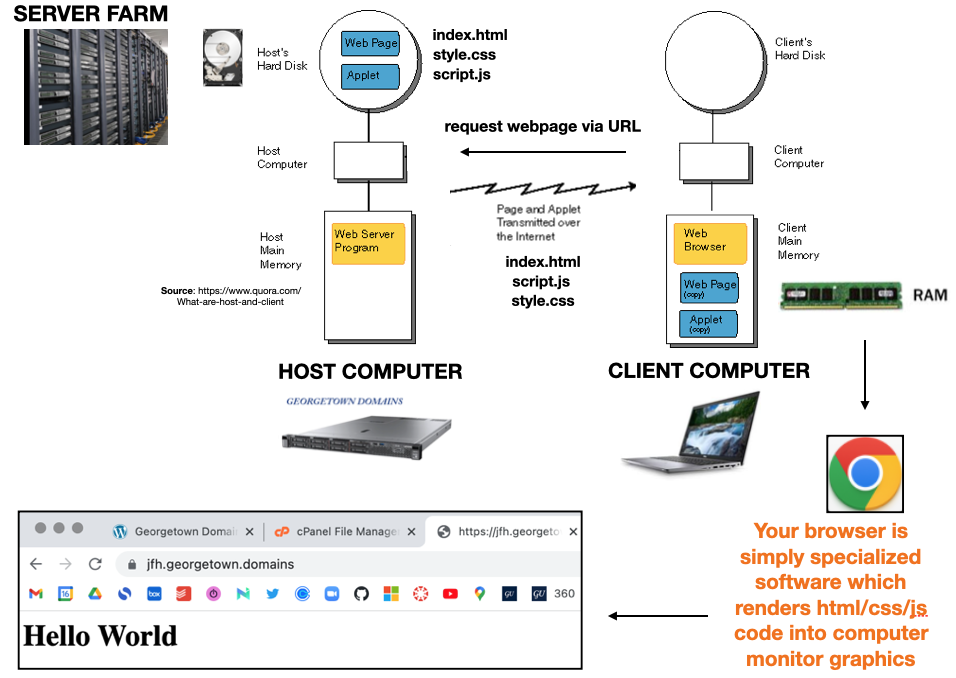
- The
serveris the computer where the content “lives”, on some hard-drive - Any program using the HTTP protocol to request content from Web servers is a
client. - The browser is specialized software for rendering HTML,CSS,JS content.
![]()
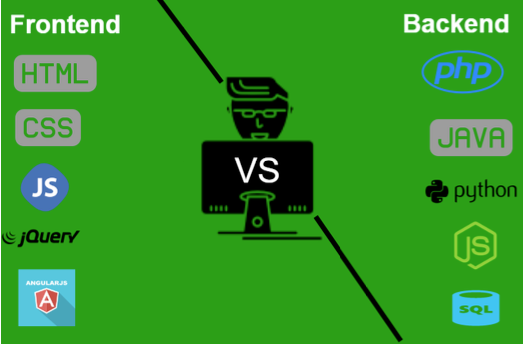
Client side vs. server side
- Scripts associated with a website can run in one of two places
- Client side, also called the front-end
- e.g. Your laptop
- Server side, also called the back-end
- e.g. The GU-domains server
- Full-stack=Front-end+Back-end
- Client side, also called the front-end
- The DSAN program is NOT a “web development” or “software engineering” program, however, many of the skills over-lap.
- It is useful to understand HTML/CSS/JS at an intermediate level, which can increase your marketability
Webpages
- The core technologies fundamental to all websites are HTML, CSS, Java-script (JS).
- HTML: The markup language used to structure web content, e.g. paragraphs, headings, and data tables, or embedding images and videos in the page.
![]()
- CSS: The language of style rules for customizing our HTML content, e.g. setting background colors, fonts, and laying content.
![]()
- JavaScript: Scripting language that enables programmatic modification of content, control multimedia, animate images, and pretty much everything else.
![]()
Source: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Learn/JavaScript/First_steps/What_is_JavaScript
JavaScript
- Many formats do not allow dynamic (interactive) content (e.g. png, jpeg, etc), however,
htmlcan be dynamically and programmatically updated - This modification is done via JavaScript (js), which dramatically expands the functionality of a html.
- JavaScript runs after the webpage is loaded and facilitates interactivity.
- It enables almost all of the advanced visualization libraries that we will discuss later

We won’t cover much Java-Script in the DSAN program, but will discuss it more in DSAN-5200 in the context of interactive data visualization
Front-end Dev Tools
HTML and DOM
Document object model (DOM)
HTML elements
- Fundamental HTML building block
- Start tag, content, end tag
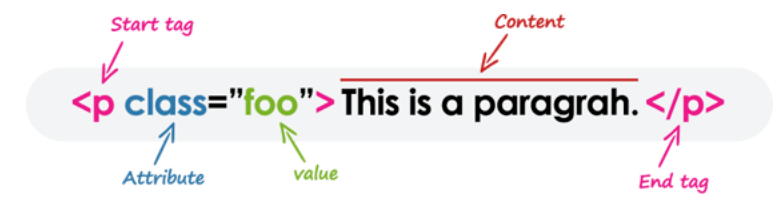
HTML attributes
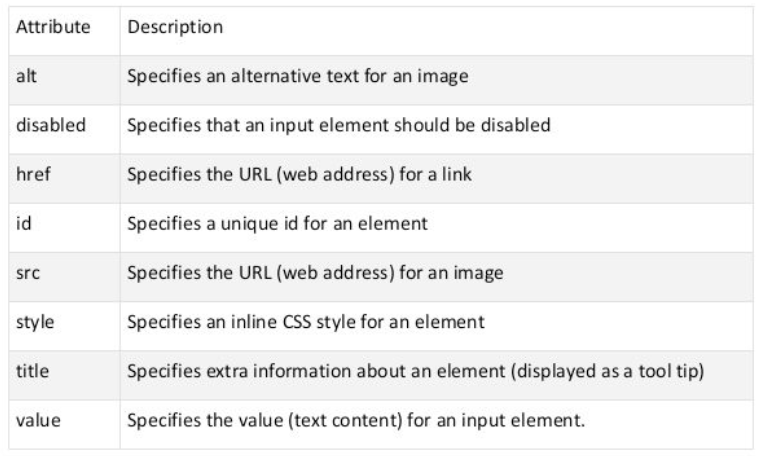
- HTML attributes are added to the opening tag of an element to change the element’s default behavior.
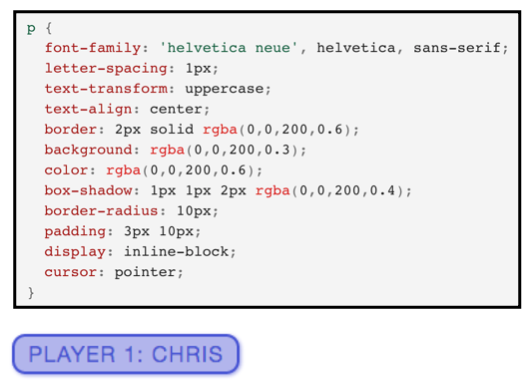
- Here we are modifying the \(<p>\) (paragraph) element with a unique identifier id attribute and changing the text-color using the style attribute.

HTML structure
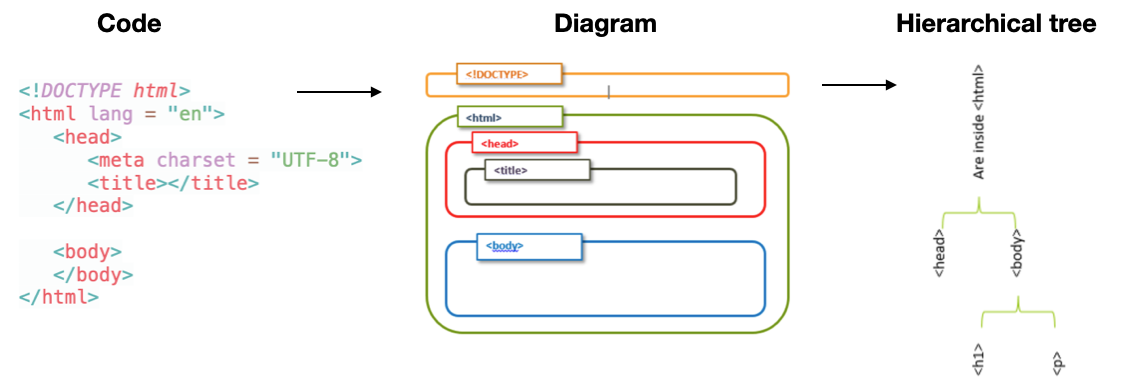
- An HTML document is a hierarchical tree-like collection of many HTML elements
![]()
- HTML elements (objects) can have parents, grandparents, siblings, children, grandchildren, etc.
Document object model:
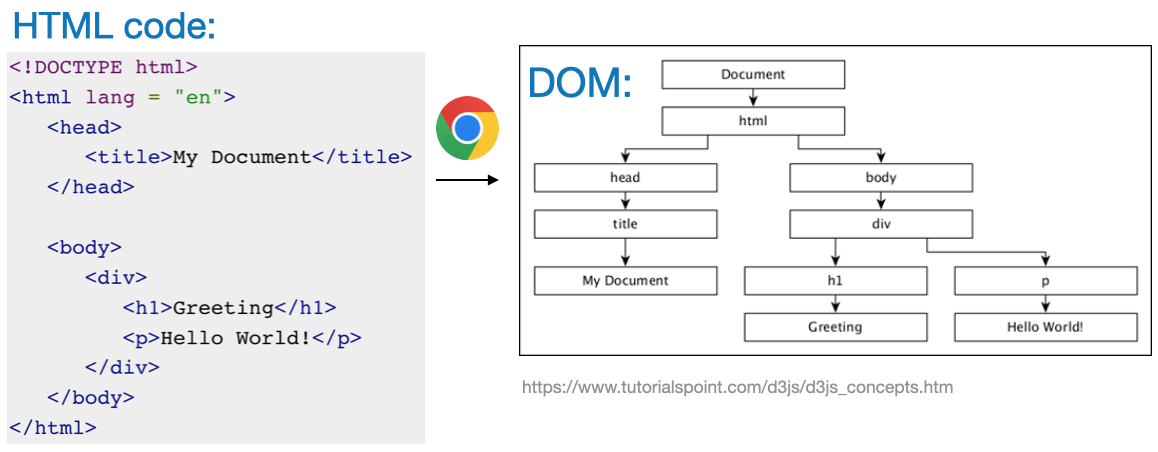
- What is it? The Document Object Model (DOM) is a cross-platform and language-independent interface. It treats an XML or HTML document as a tree structure, where each node is an object, representing a part of the document. source
- The DOM represents a document as a logical tree, this concept facilitates programmatic access and modification of the tree (add/modify/remove)
- When an HTML page is loaded by a browser, it is converted to a hierarchical structure
- HTML tags are converted into an objects in the DOM within the parent-child hierarchy
![]()
Lab Time!
Getting HTML onto the Internet
Getting Quarto onto the Internet
Python Coding Fundamentals
Types of Languages
- Compiled
- Interpreted
Primitive Types
- Boolean (
TrueorFalse) - Numbers (Integers, Decimals)
- Strings
None
Stack and Heap
Let’s look at what happens, in the computer’s memory, when we run the following code:
Algorithmic Thinking
- What are the inputs?
- What are the outputs?
- Standard cases vs. edge cases
- Adversarial development: brainstorm all of the ways an evil hacker might break your code!
Example: Finding An Item Within A List
- Seems straightforward, right? Given a list
l, and a valuev, return the index oflwhich containsv - Corner cases galore…
- What if
lcontainsvmore than once? What if it doesn’t containvat all? What iflisNone? What ifvisNone? What iflisn’t a list at all? What ifvis itself a list?
Python: #1 Sanity-Preserving Tip!
- (For our purposes) the answer to “what is Python?” is: an executable file that runs
.pyfiles!- e.g., we can run
python mycode.pyin Terminal/PowerShell
- e.g., we can run
- Everything else:
pip, Jupyter, Pandas, etc., is an add-on to this basic functionality!
Code Blocks via Indentation
0
1
2
3
4Cell In[3], line 2 print(i) ^ IndentationError: expected an indented block after 'for' statement on line 1
DSAN 5000 W02: Nuts and Bolts for Data Science